

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Group 18 : NMR active nuclei
المؤلف:
CATHERINE E. HOUSECROFT AND ALAN G. SHARPE
المصدر:
INORGANIC CHEMISTRY
الجزء والصفحة:
2th ed p 495
4-3-2017
1877
Group 18 : NMR active nuclei
In the NMR spectroscopic characterization of Xecontaining compounds, use is made of 129Xe, with a natural abundance of 26.4% and I = 1/2. Although direct observation of 129Xe is possible, the observation of satellite peaks in, for example, 19F NMR spectra of xenon fluorides is a valuable diagnostic tool as we illustrated for [XeF5]- .
Worked example : NMR spectroscopy of xenon-containing compounds
Reaction of XeF4 and C6F5BF2 at 218K yields [C6F5XeF2][BF4]. (a) Use VSEPR theory to suggest a structure for [C6F5XeF2]+. (b) The 129Xe NMR spectrum of [C6F5XeF2][BF4] consists of a triplet (J = 3892 Hz), and the 19F NMR spectrum shows a three-line signal (relative intensities ≈ 1 : 5.6 : 1), three multiplets and a singlet. The relative integrals of the five signals are 2 :2 :1 :2 : 4. Rationalize these data.
(a) Xe has eight valence electrons. The positive charge can be formally localized on Xe,
leaving seven valence electrons. Each F atom provides one electron to the valence shell of Xe. The C6F5 group is bonded through carbon to Xe and provides one electron to the valence shell of Xe.
Total number of electrons in the valence shell of Xe=10 The parent shape for [C6F5XeF2]+ is a trigonal bipyramid with the two lone pairs in the equatorial plane to minimize lone pair–lone pair repulsions. For steric reasons, the C6F5 group is expected to lie in the equatorial plane with the plane of the aryl ring orthogonal to the plane containing the XeF2 unit. The expected structure is T-shaped:
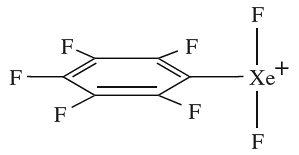
(b) The triplet in the 129Xe NMR spectrum of [C6F5XeF2][BF4] shows a large coupling constant (3892 Hz) and arises from coupling between 129Xe and the two equivalent, directly bonded 19F nuclei.
There are four F environments in [C6F5XeF2]+ (ortho, meta and para-F atoms in the aryl group and the two equivalent F atoms bonded to Xe, with a ratio 2:2:1:2, respectively. The signals for the aryl F atoms appear as multiplets because of 19F–19F coupling between non-equivalent F atoms. There are four equivalent F atoms in the [BF4]- ion leading to a singlet; coupling to 11B is not observed. Only the directly bonded 19F nuclei couple to 129Xe (I = 1 2, 26.4%). The signal
in the 19F NMR spectrum assigned to these F atoms appears as a singlet with satellites for the 26.4% of the 19F bonded to spin-active 129Xe. The relative intensities 1 :5.6 :1 correspond to 26.4% of the signal split into a doublet.
 الاكثر قراءة في الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر
الاكثر قراءة في الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















