

تاريخ الرياضيات

الاعداد و نظريتها

تاريخ التحليل

تار يخ الجبر

الهندسة و التبلوجي


الرياضيات في الحضارات المختلفة

العربية

اليونانية

البابلية

الصينية

المايا

المصرية

الهندية


الرياضيات المتقطعة

المنطق

اسس الرياضيات

فلسفة الرياضيات

مواضيع عامة في المنطق


الجبر

الجبر الخطي

الجبر المجرد

الجبر البولياني

مواضيع عامة في الجبر

الضبابية

نظرية المجموعات

نظرية الزمر

نظرية الحلقات والحقول

نظرية الاعداد

نظرية الفئات

حساب المتجهات

المتتاليات-المتسلسلات

المصفوفات و نظريتها

المثلثات


الهندسة

الهندسة المستوية

الهندسة غير المستوية

مواضيع عامة في الهندسة

التفاضل و التكامل


المعادلات التفاضلية و التكاملية

معادلات تفاضلية

معادلات تكاملية

مواضيع عامة في المعادلات


التحليل

التحليل العددي

التحليل العقدي

التحليل الدالي

مواضيع عامة في التحليل

التحليل الحقيقي

التبلوجيا

نظرية الالعاب

الاحتمالات و الاحصاء

نظرية التحكم

بحوث العمليات

نظرية الكم

الشفرات

الرياضيات التطبيقية

نظريات ومبرهنات


علماء الرياضيات

500AD

500-1499

1000to1499

1500to1599

1600to1649

1650to1699

1700to1749

1750to1779

1780to1799

1800to1819

1820to1829

1830to1839

1840to1849

1850to1859

1860to1864

1865to1869

1870to1874

1875to1879

1880to1884

1885to1889

1890to1894

1895to1899

1900to1904

1905to1909

1910to1914

1915to1919

1920to1924

1925to1929

1930to1939

1940to the present

علماء الرياضيات

الرياضيات في العلوم الاخرى

بحوث و اطاريح جامعية

هل تعلم

طرائق التدريس

الرياضيات العامة

نظرية البيان
Domain and Range
المؤلف:
المرجع الالكتروني للمعلوماتيه
المصدر:
www.almerja.com
الجزء والصفحة:
...
4-3-2017
9381
When working with functions, we frequently come across two terms: DOMAIN & RANGE. What is a domain? What is a range? Why are they important?
Definition
Domain: The domain of a function is the set of all possible input values (often the "x" variable), which produce a valid output from a particular function. It is the set of all real numbers for which a function is mathematically defined.
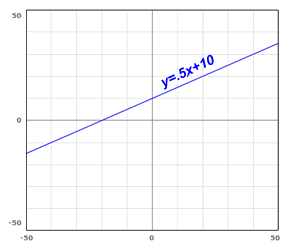
Most often a simple function's domain is all real numbers. Consider a simple linear equation like the graph shown below drawn from the function y=.5x+10. What values are valid inputs? It's not a trick question -- every real number! Its range is all real numbers because there is nothing you can put in for x that won't work. That's why the graph extends forever in the x directions (left and right).
What kind of functions don't have a domain of all real numbers? Well, if the domain is the set of all real numbers for which the function is defined, then logically we're looking for a function that has certain input values that do not produce a valid output, i.e., the function is undefined for that input. Here is an example:
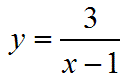
This function is defined for almost any real x. But, what is the value of y when x=1? Well, it's 3 divided by 0, which is undefined. Therefore 1 is not in the domain of this function. All other real numbers are valid inputs, so the domain is all real numbers except for x=1.
What other kinds of functions have domains that aren't all real numbers? Certain "inverse" functions, like the inverse trig functions, have limited domains as well. Since the sine function can only haveoutputs from -1 to 1, its inverse can only accept inputs from -1 to 1. The domain of inverse sine is -1 to 1. However, the most common reason for limited domains is probably the divide by zero issue. When finding the domain of a function, first look for any values that cause you to divide by zero. Remember also that we cannot take the square root of a negative number, so keep an eye out for situations where the radicand (the "stuff" inside the square root sign) could result in a negative value. In that case, it would not be a valid input so the domain would not include such values.
Definition
Range: The range is the set of all possible output values (usually the variable y, or sometimes expressed as f(x)), which result from using a particular function.
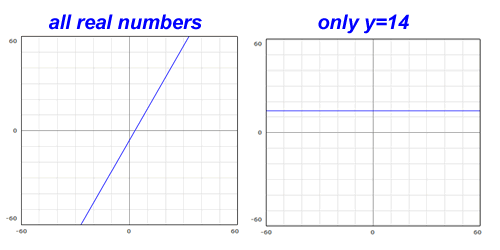
The range of a simple linear function is almost always going to be all real numbers. A graph of a line, such as the one shown below on the left, will extend forever in either y direction. There's one notable exception: y=constant. When you have a function where y equals a constant (like y=3), your graph is a horizontal line. In that case, the range is just that one value. Otherwise, the range is all real numbers.
Many other functions have limited ranges. While only a few types have limited domains, you will frequenty see functions with unusual ranges. Here are a few examples:
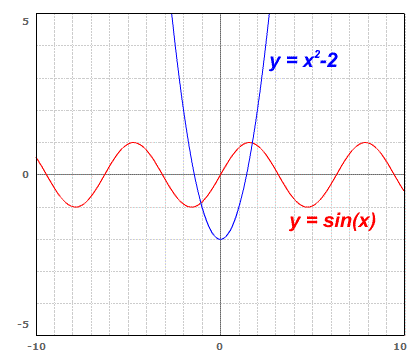
As you can see, these two functions have ranges that are limited. No matter what values you enter into a sine function you will never get a result greater than 1 or less than -1. No matter what values you enter into y=x2−2 you will never get a result less than -2.
Summary: The domain of a function is all the possible input values for which the function is defined, and the range is all possible output values.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الجبر
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الجبر
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















