

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Beryllium organometallics
المؤلف:
CATHERINE E. HOUSECROFT AND ALAN G. SHARPE
المصدر:
INORGANIC CHEMISTRY
الجزء والصفحة:
2th ed p 507
28-2-2017
2580
Beryllium organometallics
Beryllium alkyls and aryls are best made by reaction types 1.1 and 1.2 respectively. They are hydrolysed by water and inflame in air.
 (1.1)
(1.1)
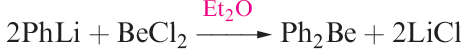 (1.2)
(1.2)
In the vapour phase, Me2Be is monomeric, with a linear C_Be_C unit (Be_C = 170pm) . The solid state structure is polymeric (1.1), and resembles that of BeCl2. However, whereas the bonding in BeCl2 can be described in terms of a localized bonding scheme , there are insufficient valence electrons available in (Me2Be)n for an analogous bonding picture. Instead, 3c-2e bonds are invoked as described for BeH2. Higher alkyls are progressively polymerized to a lesser extent, and the tert-butyl derivative is monomeric under all conditions.
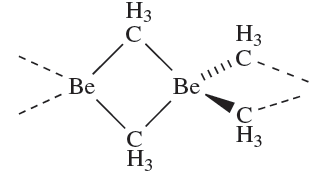
(1.1)
 (1.3)
(1.3)
Reaction 1.3 leads to the formation of Cp2Be, and in the solid state, the structure (Figure 1.1a) is in accord with the description (η1-Cp)(η5-Cp)Be. Electron diffraction and spectroscopic studies of Cp2Be in the gas phase have provided conflicting views of the structure, but recent data indicate that it resembles that found in the solid state rather than the (η5-Cp)2Be originally proposed. In solution, however, the 1H NMR spectrum shows that all proton environments are equivalent even at 163 K.
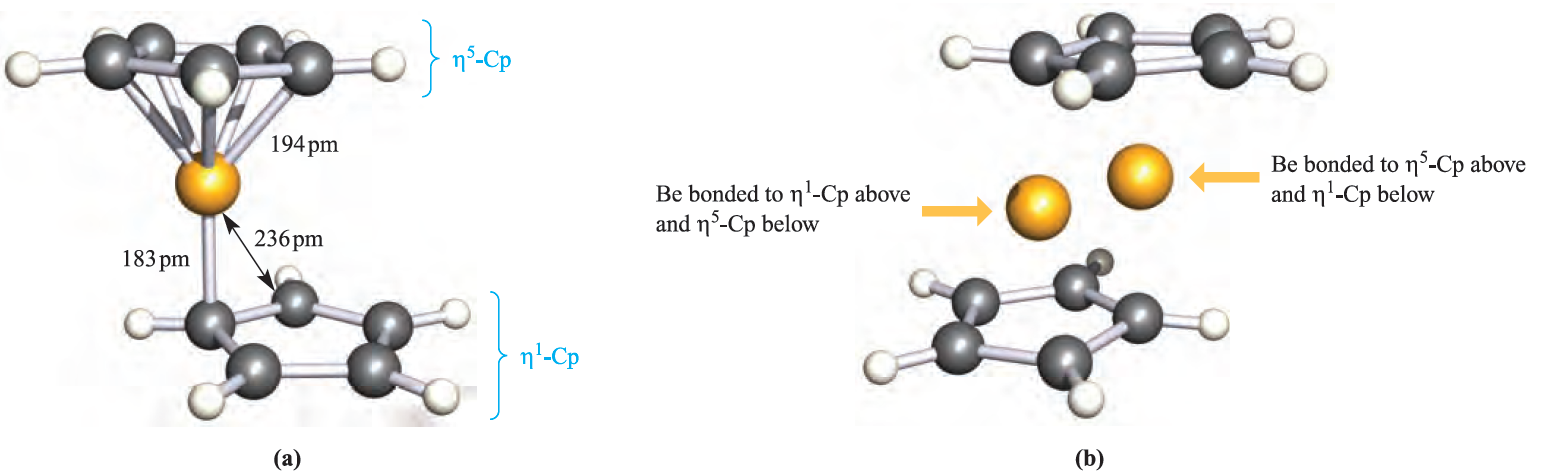
Fig. 1.1 (a) The solid state structure of Cp2Be determined by X-ray diffraction at 128K [K.W. Nugent et al. (1984) Aust. J. Chem., vol. 37, p. 1601]. (b) The same structure showing the two equivalent sites over which the Be atom is disordered. Colour code: Be, yellow; C, grey; H, white.
Furthermore, the solid state structure is not as simple as Figure 1.1a shows; The compound (C5HMe4)2Be can be prepared at room temperature from BeCl2 and K[C5HMe4]. In the solid state at 113 K, it is structurally similar to Cp2Be although, in (C5HMe4)2Be, the Be atom is not disordered. Solution 1H NMR spectroscopic data for (C5HMe4)2Be are consistent with the molecule being fluxional down to 183 K. The fully methylated derivative (C5Me5)2Be is made by reaction 1.4. In contrast to Cp2Be and (C5HMe4)2Be, (C5Me5)2Be possesses a sandwich structure in which the two C5-rings are coparallel and staggered (Figure 1.2), i.e. the compound is formulated as (η5-C5Me5)2Be.

Fig. 1.2 The solid state structure (X-ray diffraction at 113 K) of (η5-C5Me5)2Be [M. del Mar Conejo et al. (2000) Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., vol. 39, p. 1949]. Colour code: Be, yellow; C, grey; H, white.
 (1.4)
(1.4)
In a sandwich complex, the metal centre lies between two π-bonded hydrocarbon (or derivative) ligands. Complexes of the type (η5-Cp)2M are called metallocenes.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















