

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
The Brønsted-Lowry Acid-Base Theory
المؤلف:
John T. Moore, EdD
المصدر:
Chemistry Essentials For Dummies
الجزء والصفحة:
p 146
26-1-2017
2062
The Brønsted-Lowry Acid-Base Theory
Here’s how the Brønsted-Lowry theory defines acids and bases:
✓ An acid is a proton (H+) donor
✓ A base is a proton (H+) acceptor
The base accepts the H+ by furnishing a lone pair of electrons for a coordinate-covalent bond, which is a covalent bond (shared pair of electrons) in which one atom furnishes both of the electrons for the bond. Normally, one atom furnishes one electron for the bond and the other atom furnishes the second electron . In the coordinate-covalent bond, one atom furnishes both bonding electrons. Figure 1-1 shows the NH3/HCl reaction using the electron-dot structures of the reactants structures and products.
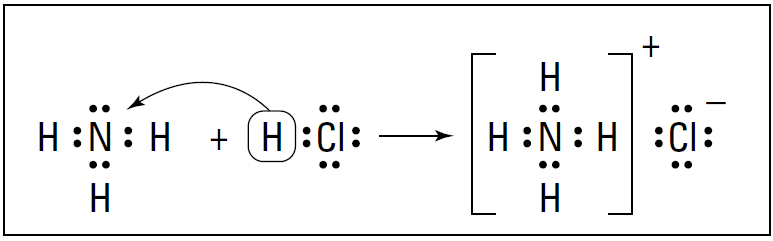
Figure 1-1: Reaction of NH3 with HCl.
HCl is the proton donor, and the acid and ammonia are the proton acceptor, or the base. Ammonia has a lone pair of nonbonding electrons that it can furnish for the coordinatecovalent bond.
 الاكثر قراءة في مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء
الاكثر قراءة في مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















