
SYMBOLIC LOGIC AND THE ALGEBRA OF PROPOSITIONS-Indirect proofs
 المؤلف:
J. ELDON WHITESITT
المؤلف:
J. ELDON WHITESITT
 المصدر:
BOOLEAN ALGEBRA AND ITS APPLICATIONS
المصدر:
BOOLEAN ALGEBRA AND ITS APPLICATIONS
 الجزء والصفحة:
65-67
الجزء والصفحة:
65-67
 9-1-2017
9-1-2017
 1560
1560
The simplest indirect proof is an application of the fact that any implication p→q is equivalent to its contrapositive q' →p'. For example, suppose that we wish to establish the implication "if x2 is an odd integer, then .r is an odd integer." The following is an indirect proof. Assume that x = 2n is an even integer. Then x2 = 4n2, an even integer, and this completes the proof.
More generally, we define an indirect proof of the validity of a given argument to be any valid argument which has for premises one or more premises of the given argument and the negation of the given conclusion, and for a conclusion either the negation of a given premise or the negation of any known true proposition. For example, the argument with premises p1, p2, . . . , pn and conclusion q is valid if we can show that a second argument with premises p1, p2,p3 . . . , pn and conclusion pi is valid.
Any of the arguments used as indirect proofs and according to the definition are equivalent to the given argument. While we will not prove this statement in general, the method of proof for any given case is illustrated by the following example.
EXAMPLE 1. In attempting to show that the argument
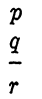
is valid, suppose that the argument
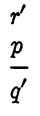
has been shown to be valid. This is an example of an indirect proof. To show that this is equivalent to the direct method, we note that the validity of the second argument means that r'p → q' is a tautology. But r'p →q' is equal to r + p' + q', and this in turn is equal to pq → r, which must also be a tautology. Hence, the original argument is valid by the definition of validity.
EXAMPLE 2. Test the following argument for validity:
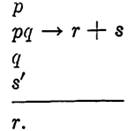
Note. when →is used between expressions involvin + , or . the grouping will henceforth be assumed to follow the same rules as if the→ were the symbol =. For example, pq →r +s means (pq) → (r + s).
Solution. We will take as premises for the indirect proof all given premises except s', and the negation of the conclusion, r'. The indirect argument, in steps, follows:

But this conclusion is the negation of the premise s', hence the given argument is valid.
A special type of proof arises in attempting to show that a given implication is false. The obvious method is to prove that the negation of the given implication is true. However, if the implication concerns a property of a set of objects, it is often easy to disprove the implication by exhibiting a specific element of the set for which the proposition is false. Such a proof is called a proof by counterexample.
 الاكثر قراءة في الجبر البولياني
الاكثر قراءة في الجبر البولياني
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


