

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Double displacement reactions
المؤلف:
John T. Moore, EdD
المصدر:
Chemistry Essentials For Dummies
الجزء والصفحة:
p 95
9-1-2017
2127
Double displacement reactions
In single displacement reactions (see the preceding section), only one chemical species is displaced. In double displacement reactions, or metathesis reactions, two species (normally ions) are displaced. Most of the time, reactions of this type occur in a solution, and either an insoluble solid (in precipitation reactions) or water (in neutralization reactions) will be formed.
Precipitation reactions: Forming solids
The formation of an insoluble solid in a solution is called precipitation. For instance, if you mix a solution of potassium chloride and a solution of silver nitrate, a white insoluble solid forms in the resulting solution. Here are the molecular, ionic, and net-ionic equations for this double-displacement reaction:
Molecular: KCl(aq) + AgNO3(aq) → AgCl(s) + KNO3(aq)
Ionic: K+ + Cl– + Ag+ + NO3– → AgCl(s) + K+ + NO3–
Net-ionic: Cl– + Ag+ → AgCl(s)
The white insoluble solid that forms (AgCl) is silver chloride. You can drop out the potassium cation and nitrate anion spectator ions, because they don’t change during the reaction and are found on both sides of the equation in an identical form. To write these equations, you have to know something about the solubility of ionic compounds:
✓ If a compound is soluble, it will not react at all and you can represent it by the appropriate ions or use (aq).
✓ If a compound is insoluble, it will precipitate (form a solid).
Table 1-1 Solubilities of Selected Ionic Compounds
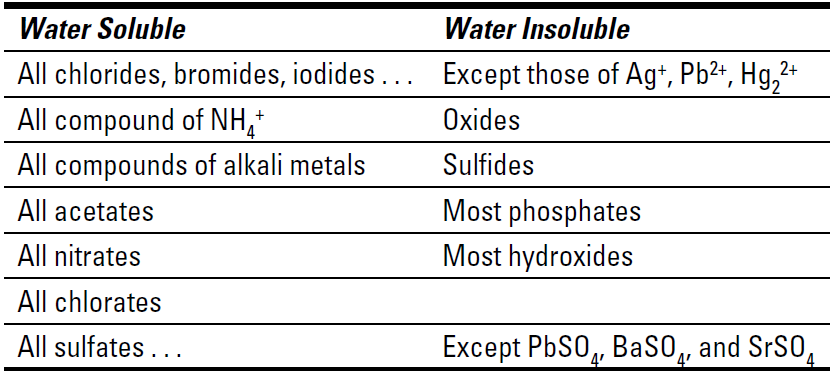
To use Table 1-1, take the cation of one reactant and combine it with the anion of the other reactant (and vice versa), keeping the neutrality of the compounds. This allows you to predict the possible products of the reaction. Then look up the solubilities of the possible products in the table. If the compound is insoluble, it’ll precipitate. If it’s soluble, it’ll remain in solution.
Neutralization reactions: Forming water
Besides precipitation the other type of double-displacement reaction is the reaction between an acid and a base. This double-displacement reaction, called a neutralization reaction, forms water.
Take a look at the mixing solutions of sulfuric acid (auto battery acid, H2SO4) and sodium hydroxide (lye, NaOH). Here are the molecular, ionic, and net-ionic equations for this reaction:
Molecular: H2SO4(aq) + 2 NaOH(aq) → Na2SO4(aq) + 2 H2O(l)
Ionic: 2H+ + SO42– + 2Na+ + 2OH– → 2Na+ + SO42– + 2H2O(l)
Net-ionic: 2H+ + 2OH– → 2H2O(l) or H+ + OH– → H2O(l)
To go from the ionic equation to the net-ionic equation, you let the spectator ions (those that don’t really react and that appear in an unchanged form on both sides on the arrow) drop out. Then reduce the coefficients in front of the reactants and products down to the lowest common denominator.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















