
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
Quantum Computer
المؤلف:
Franklin Potter and Christopher Jargodzki
المصدر:
Mad about Modern Physics
الجزء والصفحة:
p 79
1-11-2016
704
Quantum Computer
The new quantum computers rely on quantum coherence. That is, the quantum computer system contains N identical quantum subsystems for example, atoms, or optical setups, or molecules, or resonant cavities. In general, each quantum subsystem can be in many possible quantum states. Assume that the ψi for each quantum subsystem has only two states, which we label 1 and 0. If N = 3, then Ψ = ψ1 + ψ2 + ψ3 is the QM state of the system. Therefore our quantum computer represents all eight states simultaneously: 000, 001, 010, 011, 100, 101, 110, 111.
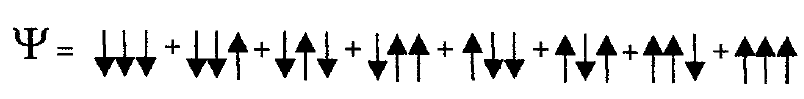
That is, during calculations on Ψ all eight states participate in each calculation! If the quantum computer is actually a large molecule in a vacuum, then the molecule must be kept away from the walls of the container and away from other molecules. Why?
Answer
A quantum computer relies on maintaining its linear superposition of quantum states—that is, Ψ = ψ1 + ψ2 + ψ3, its coherence during the calculations so that all the states participate in the calculation. Quantum decoherence is a bad thing for a quantum computer. A collision with the wall of the chamber or with another molecule will ruin the coherence because an observation has been made. By QM rule 3, we no longer sum over the amplitudes ψi. This decoherence then ruins the quantum computation because only one state will be participating in the computations.
Maintaining coherence in a real physical system has been progressing slowly for the past decade, with coherence times of tens of nanoseconds for three identical subsystems working as a quantum computer. No one knows what type of physical system will compose the first 18-subsystem quantum computer in the future, but this computer probably will outdo all the other classical computers combined in computing speed.
 الاكثر قراءة في طرائف الفيزياء
الاكثر قراءة في طرائف الفيزياء
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















