
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
Graphite
المؤلف:
Franklin Potter and Christopher Jargodzki
المصدر:
Mad about Modern Physics
الجزء والصفحة:
p 70
20-10-2016
392
Graphite
Atoms in a crystal make a regular array if there are no dislocations. Most pure single-element crystals have a cubic or a diamond crystal structure, with all orthogonal directions showing the same structural spacing. Even for a pure element substance, however, the spacing may be different in different directions. For example, take carbon atoms, which probably are components of more than 75 percent of all known compounds. In diamond they have the same structure in all orthogonal directions, but in graphite the third direction is definitely quite different than the other two directions, which define a plane of hexagonal carbon rings. How can this third direction be so different in an originally nonbiased environment?
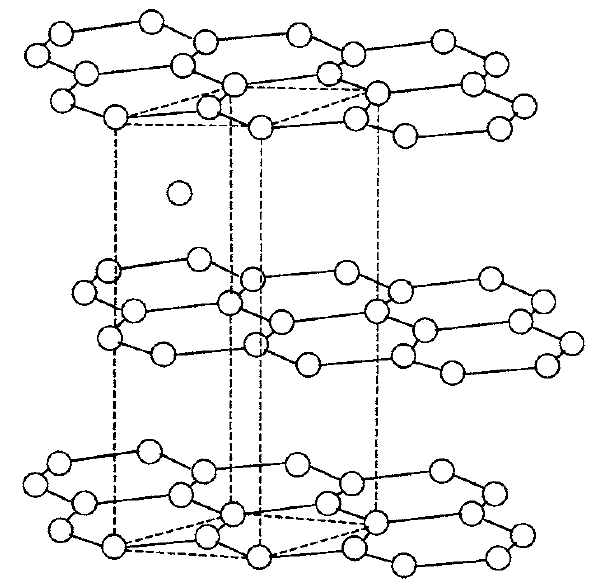
Answer
Place identical atoms into a diamond crystal structure. First, one would mathematically find a wave function for the four bonding electrons using the Schrodinger equation, resulting in what are called sp3 orbitals. Then one would represent the periodic symmetry in the crystal. Each carbon atom will make four orthogonal bonds with tetrahedral symmetry if it can to its nearest neighbors. This diamond structure is one way to do this bonding.
Another way to have four carbon bonds is for six carbon atoms to form a regular hexagonal ring with two bonds in the ring for each carbon, and the other two bonds extending perpendicular to the ring, one upward and the other downward. Upon calculating the energy states for the four carbon binding states, one learns that the two perpendicular binding states are held less securely than the ones in the ring that form a plane. The structure makes graphite, a layered crystal that slips easily between the planes. Pencil writing surfaces have been made from graphite for several thousand years.
Carbon in the fullerene structure is even more interesting. The structure of 60 carbon atoms that results depends on many factors, including the velocity distribution of the free carbon atoms before collision, the formation of intermediate structures, and so on. Fullerenes tend to form by “rolling up” a graphite sheet and adding carbon pentagons to achieve curvature. If you just roll the sheet into a cylinder and cap off the ends with pentagon-curved hemispheres, you make a carbon nanotube. These nanotubes are quite different from the traditional fullerene-type materials (i.e., roundish cages), so they have quite different properties.
 الاكثر قراءة في طرائف الفيزياء
الاكثر قراءة في طرائف الفيزياء
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام) قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى)
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى) قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى)
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى)

















