
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء والفلسفة

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
Fractional Dimensions?
المؤلف:
Franklin Potter and Christopher Jargodzki
المصدر:
Mad about Modern Physics
الجزء والصفحة:
p 24
7-10-2016
942
Fractional Dimensions?
A point has zero dimensions. A line has one dimension. A plane has two dimensions. Space has three dimensions. Can something have 1.585 . . . spatial dimensions?
Answer
Yes. Non-integer dimensions are known as fractal dimensions. A pathway toward understanding fractal dimensions begins by considering duplications of well-known objects. A line segment can be duplicated to produce two line segments. A square can be duplicated in each direction to produce four squares. A cube can be duplicated in each of its three directions to produce eight cubes. In each case we obtain the number 2 raised to an integer power. We can make a table and generalize to d arbitrary dimensions.
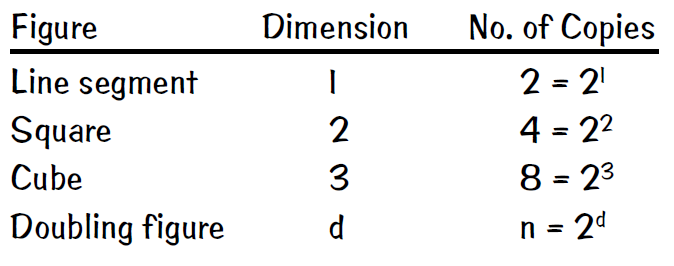
We can now determine the dimension of an interesting but strange geometrical object, the Sierpinski triangle, named after the Polish mathematician who originally thought it up in 1916, shown here with its holes being gray. Double the length of the sides, and you get another Sierpinski triangle, similar to the first. For example, if the first Sierpinski triangle has one-inch sides, the doubled one has two-inch sides. How many copies of the original triangle do you have? Remember that the gray triangles are holes, so we can’t count them. Ignoring the hole in the center of the double-sized Sierpinski triangle,

we learn that doubling the sides of the original gives us three copies, so 3 = 2d, where d = the dimension according to the scheme in the table. Using a calculator, one finds that its dimension d = 1.585 . . . , a non-integer!
In general, the mathematical expression for the dimension of the figure is given by the ratio of two logarithms: dimension = logarithm (number of self-similar pieces)/logarithm (magnification factor). For simplicity:
1. A dimension between 0 and 1 is supposed to correspond to the capacity of a set of points to partly fill a line without achieving it completely, out of having the whole value 1 that is needed.
2. A dimension between 1 and 2 is supposed to correspond to the capacity of a line to partly fill a plane, without achieving it completely, out of having the whole value 2 that is needed.
3. A dimension between 2 and 3 is supposed to correspond to the capacity of a surface to partly fill a volume without achieving it completely, out of having the whole value 3 that is needed.
There is a whole world of mathematics to be learned with fractal dimensions and fractal geometry and their applications to the familiar physical world. One interesting question is whether two or more objects with the same fractal dimension must be related in some fundamental way, either mathematically or physically.
 الاكثر قراءة في طرائف الفيزياء
الاكثر قراءة في طرائف الفيزياء
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















