

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Calculating Degree of Unsaturation
المؤلف:
John McMurry
المصدر:
Organic Chemistry
الجزء والصفحة:
9th - p187
10-7-2016
3936
Calculating Degree of Unsaturation
Because of its double bond, an alkene has fewer hydrogens than an alkane with the same number of carbons — CnH2n for an alkene versus CnH2n+2 for an alkane — and is therefore referred to as unsaturated. Ethylene, for example, has the formula C2H4, whereas ethane has the formula C2H6.

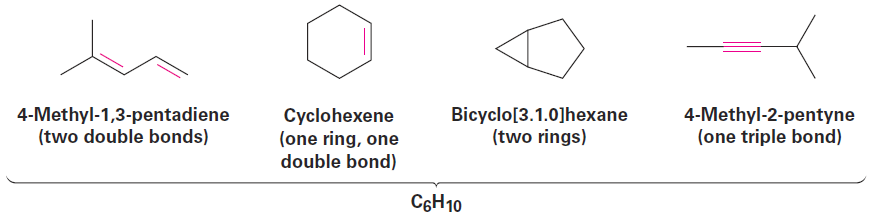
In general, each ring or double bond in a molecule corresponds to a loss of two hydrogens from the alkane formula CnH2n+2. Knowing this relationship, it’s possible to work backward from a molecular formula to calculate a molecule’s degree of unsaturation—the number of rings and/or multiple bonds present in the molecule. Let’s assume that we want to find the structure of an unknown hydrocarbon. A molecular weight determination yields a value of 82 amu, which corresponds to a molecular formula of C6H10. Since the saturated C6 alkane (hexane) has the formula C6H14, the unknown compound has two fewer pairs of hydrogens (H14 H10 = H4 = 2 H2) so its degree of unsaturation is 2. The unknown therefore contains two double bonds, one ring and one double bond, two rings, or one triple bond. There’s still a long way to go to establish its structure, but the simple calculation has told us a lot about the molecule.
Similar calculations can be carried out for compounds containing elements other than just carbon and hydrogen.
• Organohalogen compounds (C, H, X, where X= F, Cl, Br, or I) A halogen substituent acts as a replacement for hydrogen in an organic molecule, so we can add the number of halogens and hydrogens to arrive at an equivalent hydrocarbon formula from which the degree of unsaturation can be found. For example, the formula C4H6Br2 is equivalent to the hydrocarbon formula C4H8 and thus corresponds to one degree of unsaturation.
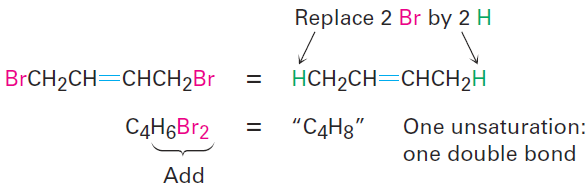
• Organooxygen compounds (C, H, O) Oxygen forms two bonds, so it
doesn’t affect the formula of an equivalent hydrocarbon and can be ignored when calculating the degree of unsaturation. You can convince yourself of this by seeing what happens when an oxygen atom is inserted into an alkane bond: C - C becomes C - O - C or C - H becomes C - O - H, and there is no change in the number of hydrogen atoms. For example, the formula C5H8O is equivalent to the hydrocarbon formula C5H8 and thus corresponds to two degrees of unsaturation.
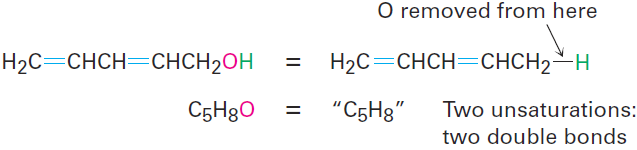
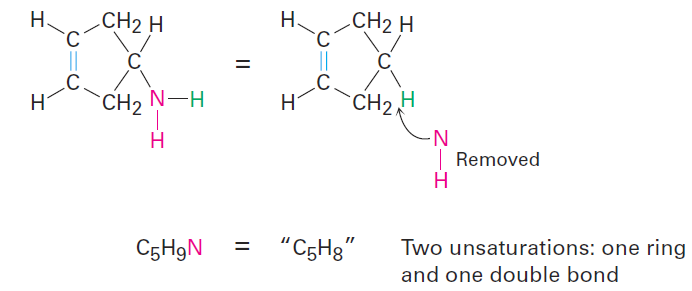
• Organonitrogen compounds (C, H, N) Nitrogen forms three bonds, so an organonitrogen compound has one more hydrogen than a related hydrocarbon. We therefore subtract the number of nitrogens from the number of hydrogens to arrive at the equivalent hydrocarbon formula. Again, you can convince yourself of this by seeing what happens when a nitrogen atom is inserted into an alkane bond: C - C becomes C - NH - C or C - H becomes C - NH2, meaning that one additional hydrogen atom has been added. We must therefore subtract this extra hydrogen atom to arrive at the equivalent hydrocarbon formula. For example, the formula C5H9N is equivalent to C5H8 and thus has two degrees of unsaturation.
 الاكثر قراءة في الهايدروكاربونات
الاكثر قراءة في الهايدروكاربونات
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















