Genetic Linkage
Two pairs of genetic markers are said to be linked when the recombination frequency between them is significantly less than 50%. The recombination frequency in a diploid that is heterozygous for two pairs of alleles is the proportion of haploid recombinants observed to the total number of haploid products examined. The genes, loci, and DNA sites affected by such alleles are also said to be. Linkage is assumed to be proof of physical location on the same chromosome.
Loci that exhibit recombination frequencies of 50% are said to be independent. Loci on different chromosomes give recombination frequencies of 50% because of the random assortment of chromosomes during meiosis; the same is true for random chromosome losses during the parasexual cycle and for the random distribution of genomic nucleic acid molecules in viruses that contain several different ones.
The recombination of alleles in two homologous DNA molecules will be observed if not just one recombination event, but any odd number of these events, occurs in the DNA segment that separates them. An even number of recombination events between them will maintain the parental configuration. The consequence is that the recombination frequency will approach 50% as the number of recombination events increases. Loci of the same chromosome will segregate independently if they are sufficiently distant and the recombination activity is sufficiently high.
Linkage disturbs Mendelian segregations as shown in Table 1. The relationship between the recombination frequency and the observed phenotype frequencies is rather complicated in the case of an F2 generation, but relatively simple in a test cross of F1 individuals with tester individuals that are homozygous for the recessive alleles at all the loci under consideration.
Table 1. Segregations of Linked Allelesa
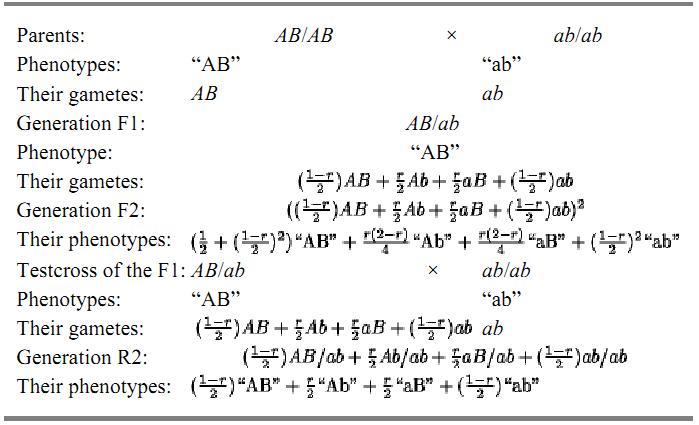
a A, a and B, b are two pairs of linked alleles. Capitals A and B are used to designate alleles with dominant phenotypes, “A” and “B,” respectively; and lower case a and b are used for alleles with recessive phenotypes, “a” and “b,” respectively. The coefficient r is the probability that a gamete from a doubly heterozygous diploid is a recombinant gamete. The percentage value is used in the construction of genetic maps.
Complete linkage—that is, zero recombination—is observed for loci located on the same chromosome in the absence of mechanisms to recombine chromosome pieces. This is the case in the males of Drosophila melanogaster, as well as in RNA viruses.
The name linkage was proposed by T. H. Morgan (1) for a phenomenon that had already been observed as a disturbance of Mendelian segregations.
References
1. T. H. Morgan (1910) Am. Nat. 44, 449.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


