
Conformations of Ethane
 المؤلف:
John McMurry
المؤلف:
John McMurry
 المصدر:
Organic Chemistry
المصدر:
Organic Chemistry
 الجزء والصفحة:
9th - p80
الجزء والصفحة:
9th - p80
 12-4-2016
12-4-2016
 3951
3951
Conformations of Ethane
Up to now, we’ve viewed molecules primarily in a two-dimensional way and have given little thought to any consequences that might arise from the spatial arrangement of atoms in molecules. Now it’s time to add a third dimension to our study. Stereochemistry is the branch of chemistry concerned with the three-dimensional aspects of molecules. We’ll see on many occasions in future chapters that the exact three-dimensional structure of a molecule is often crucial to determining its properties and biological behavior.
We know that σ bonds are cylindrically symmetrical. In other words, the intersection of a plane cutting through a carbon–carbon single-bond orbital looks like a circle. Because of this cylindrical symmetry, rotation is possible around carbon–carbon bonds in open-chain molecules. In ethane, for instance, rotation around the C-C bond occurs freely, constantly changing the spatial relationships between the hydrogens on one carbon and those on the other (Figure1).
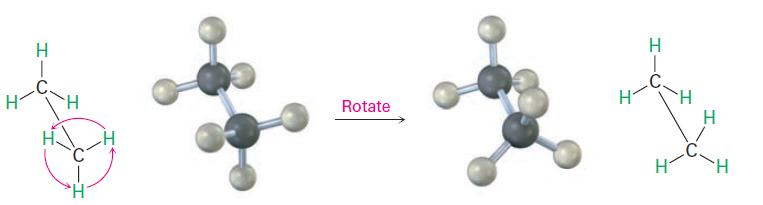
Figure1:Rotation occurs around the carbon–carbon single
bond in ethane because of s bond cylindrical symmetry.
The different arrangements of atoms that result from bond rotation are called conformations, and molecules that have different arrangements are called conformational isomers, or conformers. Unlike constitutional isomers, however, different conformers often can’t be isolated because they interconvert too rapidly. Conformational isomers are represented in two ways, as shown in Figure 2. A sawhorse representation views the carbon–carbon bond from an oblique angle and indicates spatial orientation by showing all C-H bonds. A Newman projection views the carbon–carbon bond directly end-on and represents the two carbon atoms by a circle. Bonds attached to the front carbon are represented by lines to the center of the circle, and bonds attached to the rear carbon are represented by lines to the edge of the circle.
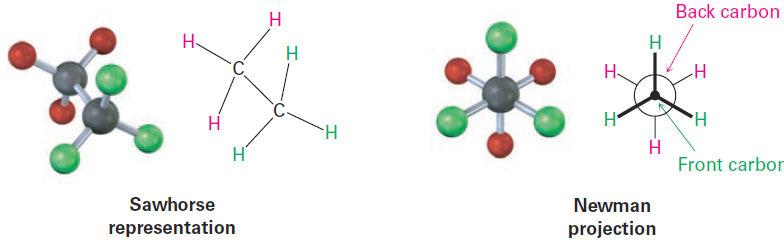
Figure 2: A sawhorse representation and a Newman projection of ethane. The sawhorse representation views the molecule from an oblique angle, while the Newman projection views the molecule end-on. Note that the molecular model of the Newman projection appears at first to have six atoms attached to a single carbon. Actually, the front carbon, with three attached green atoms, is directly in front of the rear carbon, with three attached red atoms.
Despite what we’ve just said, we actually don’t observe perfectly free rotation in ethane. Experiments show that there is a small (12 kJ/mol; 2.9 kcal/mol) barrier to rotation and that some conformations are more stable than others. The lowest-energy, most stable conformation is the one in which all six C- H bonds are as far away from one another as possible—staggered when viewed end-on in a Newman projection. The highest-energy, least stable conformation is the one in which the six C-H bonds are as close as possible— eclipsed in a Newman projection. At any given instant, about 99% of ethane molecules have an approximately staggered conformation and only about 1% are near the eclipsed conformation.
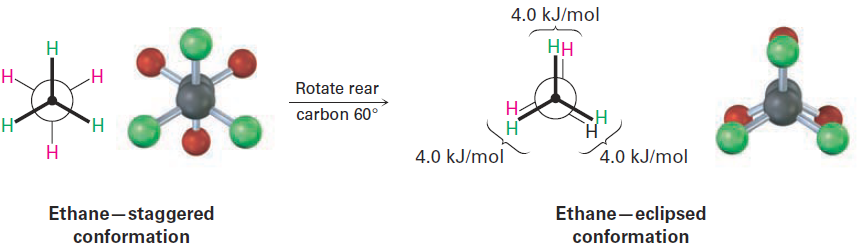
The extra 12 kJ/mol of energy present in the eclipsed conformation of ethane is called torsional strain. Its cause has been the subject of controversy, but the major factor is an interaction between C-H bonding orbitals on one carbon with antibonding orbitals on the adjacent carbon, which stabilizes the staggered conformation relative to the eclipsed one. Because a total strain of 12 kJ/mol arises from three equal hydrogen–hydrogen eclipsing interactions, we can assign a value of approximately 4.0 kJ/mol (1.0 kcal/mol) to each single interaction. The barrier to rotation that results can be represented on a graph of potential energy versus degree of rotation, in which the angle between C-H bonds on the front and back carbons as viewed end-on (the dihedral angle) goes full circle from 0 to 360°. Energy minima occur at staggered conformations, and energy maxima occur at eclipsed conformations, as shown in Figure 3.
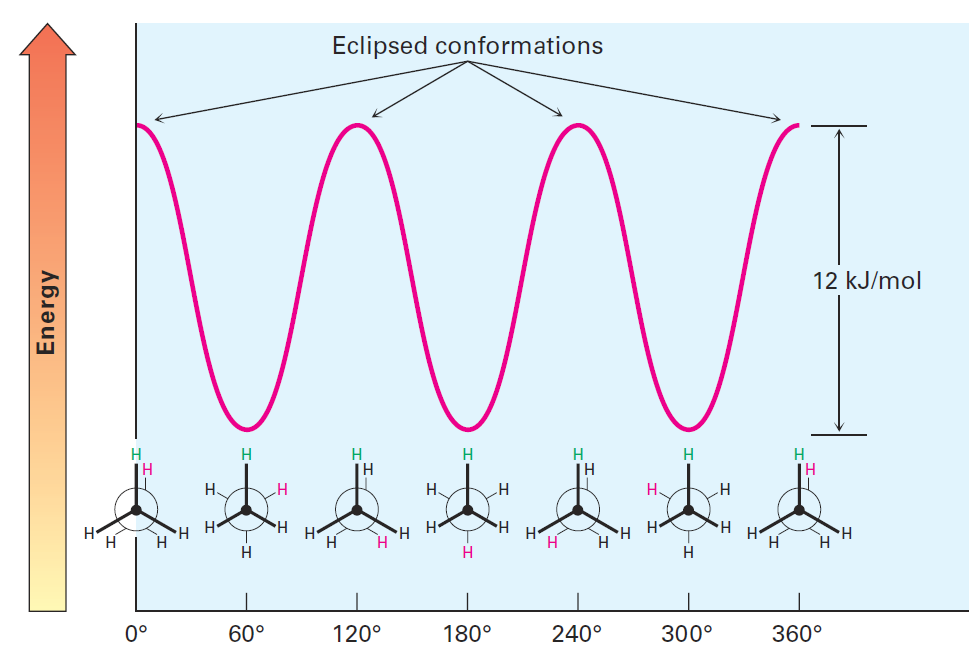
Figure 3: A graph of potential energy versus bond rotation in ethane. The staggered
conformations are 12 kJ/mol lower in energy than the eclipsed conformations.
 الاكثر قراءة في الهايدروكاربونات
الاكثر قراءة في الهايدروكاربونات
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


