
RESONATOR AS AN INTERFEROMETER
 المؤلف:
Mark Csele
المؤلف:
Mark Csele
 المصدر:
FUNDAMENTALS OF LIGHT SOURCES AND LASERS
المصدر:
FUNDAMENTALS OF LIGHT SOURCES AND LASERS
 الجزء والصفحة:
p162
الجزء والصفحة:
p162
 17-3-2016
17-3-2016
 2363
2363
RESONATOR AS AN INTERFEROMETER
In general, a laser cavity acts as an interferometer into which an integral number of waves must fit. The cavity is resonant at wavelengths such that the number of waves inside the cavity is an integer these are standing waves inside the cavity. At all other wavelengths, destructive interference causes any wave inside the cavity to be extinguished. These resonant wavelengths are called longitudinal modes and are spaced apart at regular intervals of frequency. The spacing of modes is called the free spectral range (FSR) of the interferometer and is outlined in Figure 1.1.
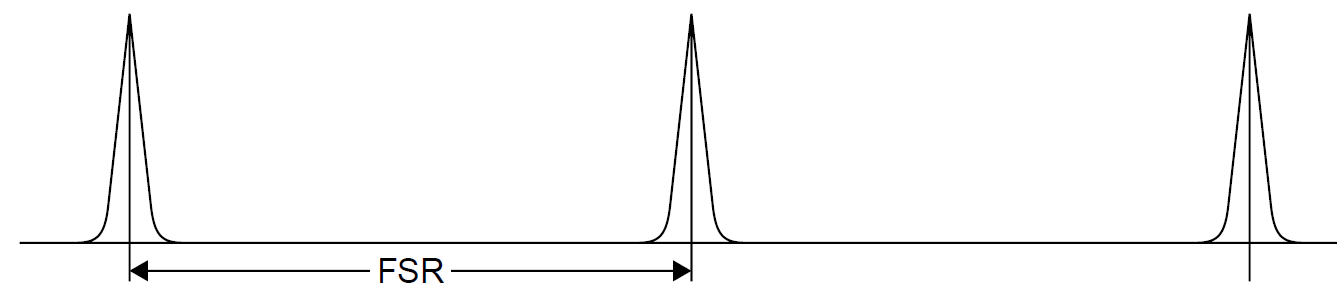
Figure 1.1. Response of an interferometer.
Assuming that the distance between the cavity mirrors is L, the condition for a standing wave in the cavity is
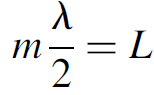 (1.1)
(1.1)
where m is an integer, so the spacing (FSR) of resonant modes in the cavity is
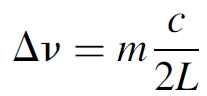 (1.2)
(1.2)
where Δv is the spacing in hertz. For any interferometer the sharpness of the resonant peaks for an interferometer is described by
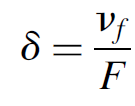 (1.3)
(1.3)
where d is the spectral width (FWHM) in hertz, vf is the frequency of the first mode (m = 1), and F is the finesse of the interferometer; it is a ratio of the mode separation (FSR) to the spectral width. Finesse is a function of the reflectivity of cavity mirrors:
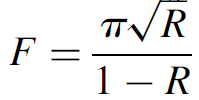 (1.4)
(1.4)
where R is the total reflectivity of both mirrors. As the reflectivity of cavity mirrors increases, the spectral width of the peaks becomes very narrow, and in most lasers the reflectivity of the cavity mirrors is very large.
Example 1.1 Argon Laser Spectral Width Computation An argon laser with a 1-m cavity spacing has an HR with a reflectivity of 99.99% and an OC with a reflectivity of 98.0%. Compute the expected spectral width of a single mode of the cavity.
SOLUTION Begin by computing the FSR as
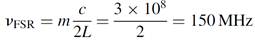
This is the spacing between resonant peaks for the interferometer. Now the finesse of the cavity may be computed first by calculating the total reflectivity of the cavity as
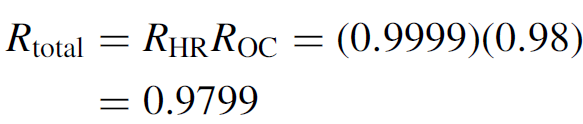
This reflectivity is then substituting into equation (1.4), allowing the calculation of finesse, in this case, 154.7. Knowing that finesse is a ratio of FSR to spectral width, spectral width can be solved by substituting into equation (1.3) to yield an answer of 969 kHz. This corresponds (using the 488-nm blue line of the argon laser) to a spectral width of 7.7 × 10-7 nm. This is an extremely narrow spectral width; however, special techniques are required to isolate a single mode from adjacent modes (which in this case are 150 MHz apart). As we shall see in this chapter, most lasers have a much larger spectral width, originating from the fact that many modes can oscillate simultaneously in most lasers.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الليزر
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الليزر
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


