

النبات

مواضيع عامة في علم النبات

الجذور - السيقان - الأوراق

النباتات الوعائية واللاوعائية

البذور (مغطاة البذور - عاريات البذور)

الطحالب

النباتات الطبية


الحيوان

مواضيع عامة في علم الحيوان

علم التشريح

التنوع الإحيائي

البايلوجيا الخلوية


الأحياء المجهرية

البكتيريا

الفطريات

الطفيليات

الفايروسات


علم الأمراض

الاورام

الامراض الوراثية

الامراض المناعية

الامراض المدارية

اضطرابات الدورة الدموية

مواضيع عامة في علم الامراض

الحشرات


التقانة الإحيائية

مواضيع عامة في التقانة الإحيائية


التقنية الحيوية المكروبية

التقنية الحيوية والميكروبات

الفعاليات الحيوية

وراثة الاحياء المجهرية

تصنيف الاحياء المجهرية

الاحياء المجهرية في الطبيعة

أيض الاجهاد

التقنية الحيوية والبيئة

التقنية الحيوية والطب

التقنية الحيوية والزراعة

التقنية الحيوية والصناعة

التقنية الحيوية والطاقة

البحار والطحالب الصغيرة

عزل البروتين

هندسة الجينات


التقنية الحياتية النانوية

مفاهيم التقنية الحيوية النانوية

التراكيب النانوية والمجاهر المستخدمة في رؤيتها

تصنيع وتخليق المواد النانوية

تطبيقات التقنية النانوية والحيوية النانوية

الرقائق والمتحسسات الحيوية

المصفوفات المجهرية وحاسوب الدنا

اللقاحات

البيئة والتلوث


علم الأجنة

اعضاء التكاثر وتشكل الاعراس

الاخصاب

التشطر

العصيبة وتشكل الجسيدات

تشكل اللواحق الجنينية

تكون المعيدة وظهور الطبقات الجنينية

مقدمة لعلم الاجنة


الأحياء الجزيئي

مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي


علم وظائف الأعضاء


الغدد

مواضيع عامة في الغدد

الغدد الصم و هرموناتها

الجسم تحت السريري

الغدة النخامية

الغدة الكظرية

الغدة التناسلية

الغدة الدرقية والجار الدرقية

الغدة البنكرياسية

الغدة الصنوبرية

مواضيع عامة في علم وظائف الاعضاء

الخلية الحيوانية

الجهاز العصبي

أعضاء الحس

الجهاز العضلي

السوائل الجسمية

الجهاز الدوري والليمف

الجهاز التنفسي

الجهاز الهضمي

الجهاز البولي


المضادات الميكروبية

مواضيع عامة في المضادات الميكروبية

مضادات البكتيريا

مضادات الفطريات

مضادات الطفيليات

مضادات الفايروسات

علم الخلية

الوراثة

الأحياء العامة

المناعة

التحليلات المرضية

الكيمياء الحيوية

مواضيع متنوعة أخرى

الانزيمات
Presence/absence method APHA 2001 for Clostridium perfringens in foods
المؤلف:
SILVA, N.D .; TANIWAKI, M.H. ; JUNQUEIRA, V.C.A.; SILVEIRA, N.F.A. , NASCIMENTO , M.D.D. and GOMES ,R.A.R
المصدر:
MICROBIOLOGICAL EXAMINATION METHODS OF FOOD AND WATE A Laboratory Manual
الجزء والصفحة:
10-3-2016
2997
Presence/absence method APHA 2001 for Clostridium perfringens in foods
Method of the American Public Health Association (APHA), as described in the 4th Edition of the Compendium of Methods for the Microbiological Examination of Foods (Labbe, 2001). Not applicable to water samples.
This method is recommended for foods likely to contain a small population of injured cells.
Caution: All the steps of the presence/absence method allow the growth (and toxin production) of Clostridium botulinum, which cannot be easily distinguished from C. perfringens. The tubes, plates, and cultures isolated during examination should be handled with care.
1 - Material required for analysis
Presumptive test
• Liver Broth
• Agar Plug (2% agar) sterile
• Tryptose Sulfite Cycloserine (TSC) Agar
• Anaerobic jars
• Anaerobic atmosphere generation systems (Anaero-gen from Oxoid, Anaerocult A from Merck, GasPak® from BD Biosciences, or equivalent)
• Laboratory incubator set to 35–37°C
Confirmation
2- Procedure
A general flowchart for the detection of Clostridium perfringens in foods using the presence/absence method APHA 2001 is shown in Figure 1.
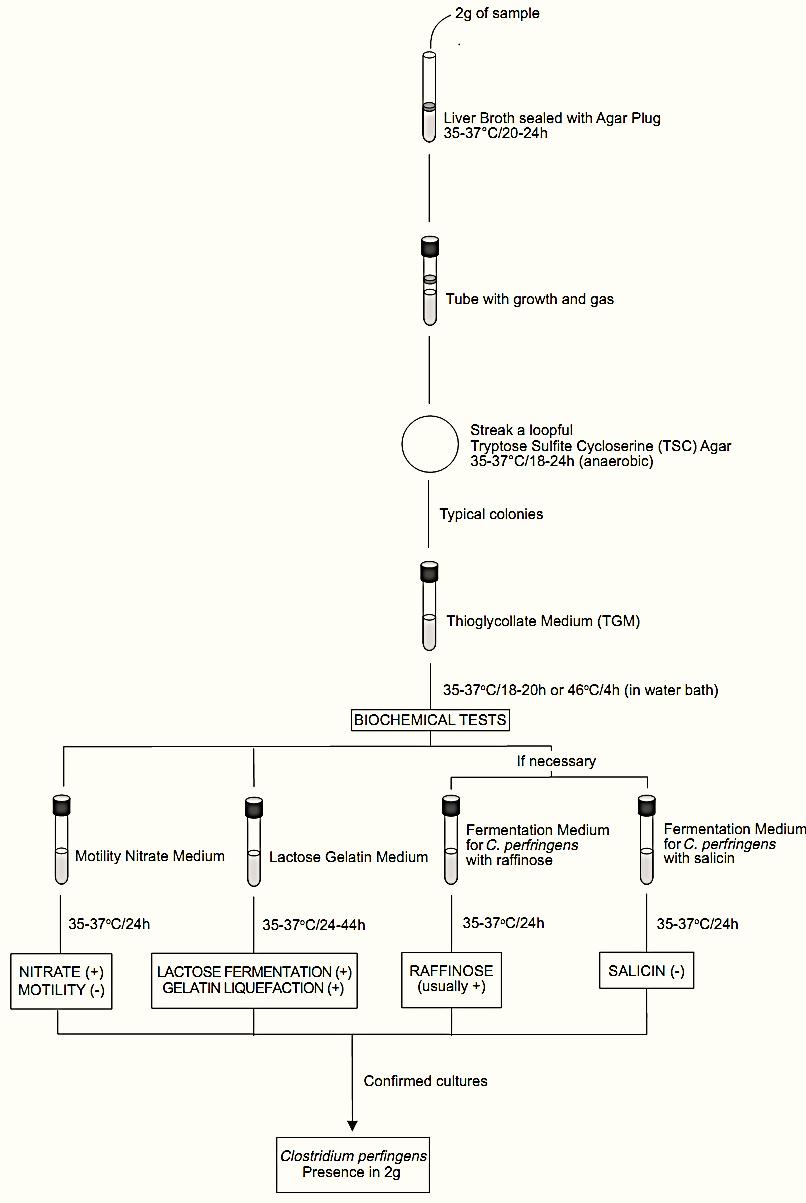
Figure 1. Scheme of analysis for the detection of Clostridium perfringens in foods using the presence/absence method APHA 2001 (Labbe, 2001).
they are supposed to be known to the analyst.
a) Inoculation and incubation. Inoculate about 2 g food sample into 15–20 ml of Liver Broth (before inoculation exhaust oxygen from Liver Broth). Over-lay the medium surface with Agar Plug (2% agar) sterile. Incubate the tubes at 35–37°C/20–24 h and examine for growth and gas production (agar plug displacement).
b) Confirmation. From each tube showing growth and gas production, streak the culture on Tryptose Sulfite Cycloserine (TSC) Agar (with or without egg yolk). Incubate the plates at 35–37°C/18–24 h under anaerobic conditions. To establish anaerobic conditions, use anaerobic atmosphere genera-tion systems (Anaerogen from Oxoid, Anaerocult A from Merck, GasPak® from BD Biosciences, or equivalent). Examine the plates for typical black C. perfringens colonies. From each plate showing growth, select at least one colony suspected to be C. perfringens and continue the procedure for confirmation, as described in the plate count method APHA 2001. Report the result as C. perfringens presence or absence in 2 g of food.
References
Silva, N.D .; Taniwaki, M.H. ; Junqueira, V.C.A.; Silveira, N.F.A. , Nasdcimento , M.D.D. and Gomes ,R.A.R .(2013) . Microbiological examination methods of food and water a laboratory Manual. Institute of Food Technology – ITAL, Campinas, SP, Brazil .
Labbe, R.G. (2001) Clostridium perfringens. In: Downes, F.P. & Ito, K. (eds.). Compendium of Methods for the Microbiological Examination of Foods. 4th edition. Washington, American Public Health Association. Chapter 34, pp. 325–330.
 الاكثر قراءة في البكتيريا
الاكثر قراءة في البكتيريا
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















