

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Subatomic Particles
المؤلف:
John T. Moore, EdD
المصدر:
Chemistry Essentials For Dummies
الجزء والصفحة:
p18
17-2-2016
3179
Subatomic Particles
The atom is the smallest part of matter that represents a particular element. For quite a while, the atom was thought to be the smallest part of matter that could exist. But in the latter part of the 19th century and early part of the 20th, scientists discovered that atoms are composed of certain subatomic particles and that no matter what the element, the same subatomic particles make up the atom. The number of the various subatomic particles is the only thing that varies.
Scientists now recognize that there are many subatomic particles (this really makes physicists salivate). But to be successful in chemistry, you really only need to be concerned with the three major subatomic particles:
✓ Protons
✓ Neutrons
✓ Electrons
Table 1 summarizes the characteristics of these three subatomic particles. The masses of the subatomic particles are listed in two ways: grams and amu, which stands for atomic mass units. Expressing mass in amu is much easier than using the gram equivalent.
Table 1 The Three Major Subatomic Particles
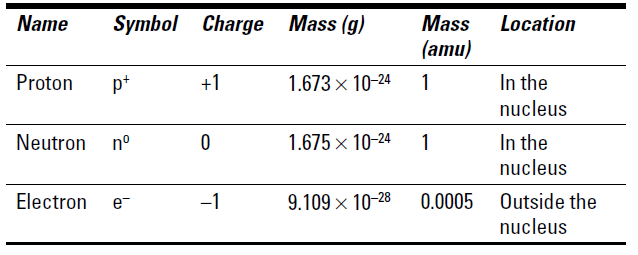
Atomic mass units are based on something called the carbon- 12 scale, a worldwide standard thatfs been adopted for atomic weights. By international agreement, a carbon atom that contains six protons and six neutrons has an atomic weight of exactly 12 amu, so 1 amu is defined as 1.12 of this carbon atom.
Because the masses in grams of protons and neutrons are almost exactly the same, both protons and neutrons are said to have a mass of 1 amu. Notice that the mass of an electron is much smaller than that of either a proton or neutron. It takes almost 2,000 electrons to equal the mass of a single proton.
Table 1 also shows the electrical charge associated with each subatomic particle. Matter can be electrically charged in one of two ways: positive or negative. The proton carries one unit of positive charge, the electron carries one unit of negative charge, and the neutron has no charge . itfs neutral. Scientists have discovered through observation that objects with like charges, whether positive or negative, repel each other, and objects with unlike charges attract each other.
The atom itself has no charge. It’s neutral. (Well, actually, certain atoms can gain or lose electrons and acquire a charge, as we explain in the later section “Ions: Varying electrons.” Atoms that gain a charge, either positive or negative, are called ions.)
So how can an atom be neutral if it contains positively charged protons and negatively charged electrons? The answer is that there are equal numbers of protons and electrons — equal numbers of positive and negative charges — so they cancel each other out. The last column in Table 1 lists the location of the three subatomic particles. Protons and neutrons are located in the nucleus, a dense central core in the middle of the atom, and the electrons are located outside the nucleus .
 الاكثر قراءة في مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء
الاكثر قراءة في مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















