

النبات

مواضيع عامة في علم النبات

الجذور - السيقان - الأوراق

النباتات الوعائية واللاوعائية

البذور (مغطاة البذور - عاريات البذور)

الطحالب

النباتات الطبية


الحيوان

مواضيع عامة في علم الحيوان

علم التشريح

التنوع الإحيائي

البايلوجيا الخلوية


الأحياء المجهرية

البكتيريا

الفطريات

الطفيليات

الفايروسات


علم الأمراض

الاورام

الامراض الوراثية

الامراض المناعية

الامراض المدارية

اضطرابات الدورة الدموية

مواضيع عامة في علم الامراض

الحشرات


التقانة الإحيائية

مواضيع عامة في التقانة الإحيائية


التقنية الحيوية المكروبية

التقنية الحيوية والميكروبات

الفعاليات الحيوية

وراثة الاحياء المجهرية

تصنيف الاحياء المجهرية

الاحياء المجهرية في الطبيعة

أيض الاجهاد

التقنية الحيوية والبيئة

التقنية الحيوية والطب

التقنية الحيوية والزراعة

التقنية الحيوية والصناعة

التقنية الحيوية والطاقة

البحار والطحالب الصغيرة

عزل البروتين

هندسة الجينات


التقنية الحياتية النانوية

مفاهيم التقنية الحيوية النانوية

التراكيب النانوية والمجاهر المستخدمة في رؤيتها

تصنيع وتخليق المواد النانوية

تطبيقات التقنية النانوية والحيوية النانوية

الرقائق والمتحسسات الحيوية

المصفوفات المجهرية وحاسوب الدنا

اللقاحات

البيئة والتلوث


علم الأجنة

اعضاء التكاثر وتشكل الاعراس

الاخصاب

التشطر

العصيبة وتشكل الجسيدات

تشكل اللواحق الجنينية

تكون المعيدة وظهور الطبقات الجنينية

مقدمة لعلم الاجنة


الأحياء الجزيئي

مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي


علم وظائف الأعضاء


الغدد

مواضيع عامة في الغدد

الغدد الصم و هرموناتها

الجسم تحت السريري

الغدة النخامية

الغدة الكظرية

الغدة التناسلية

الغدة الدرقية والجار الدرقية

الغدة البنكرياسية

الغدة الصنوبرية

مواضيع عامة في علم وظائف الاعضاء

الخلية الحيوانية

الجهاز العصبي

أعضاء الحس

الجهاز العضلي

السوائل الجسمية

الجهاز الدوري والليمف

الجهاز التنفسي

الجهاز الهضمي

الجهاز البولي


المضادات الميكروبية

مواضيع عامة في المضادات الميكروبية

مضادات البكتيريا

مضادات الفطريات

مضادات الطفيليات

مضادات الفايروسات

علم الخلية

الوراثة

الأحياء العامة

المناعة

التحليلات المرضية

الكيمياء الحيوية

مواضيع متنوعة أخرى

الانزيمات
IDENTIFICATION OF BACTERIA- Single-enzyme tests
المؤلف:
Cornelissen, C. N., Harvey, R. A., & Fisher, B. D
المصدر:
Lippincott Illustrated Reviews Microbiology
الجزء والصفحة:
3rd edition , p24
2024-12-18
1092
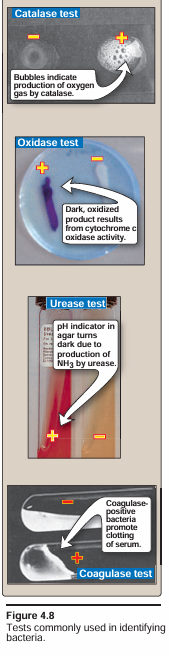
Different bacteria produce varying spectra of enzymes. For example, some enzymes are necessary for the bacterium's individual metabolism, and some facilitate the bacterium's ability to compete with other bacteria or establish an infection. Tests that measure single bacterial enzymes are simple, rapid, and generally easy to interpret. They can be performed on organisms already grown in culture and often provide presumptive identification.
1. Catalase test: The enzyme catalase catalyzes the degradation of hydrogen peroxide to water and molecular oxygen (H2O2 → H2O + O2). Catalase-positive organisms rapidly produce bubbles when exposed to a solution containing hydrogen peroxide (Figure 4.8). The catalase test is key in differentiating between many gram-positive organisms. For example, staphylococci are catalase positive, whereas streptococci and enterococci are catalase negative. The production of catalase is an important virulence factor because H2O2 is antimicrobial, and its degradation decreases the ability of neutrophils to kill invading bacteria.
2. Oxidase test: The enzyme cytochrome c oxidase is part of electron transport and nitrate metabolism in some bacteria. The enzyme can accept electrons from artificial substrates (such as a phenylenediamine derivative), producing a dark, oxidized product (see Figure 4.8). This test assists in differentiating between groups of gram-negative bacteria. Pseudomonas aeruginosa, for example, is oxidase positive.
3. Urease: The enzyme urease hydrolyzes urea to ammonia and car- bon dioxide (NH2CONH2 + H2O→ 2NH3 + CO2). The ammonia produced can be detected with pH indicators that change color in response to the increased alkalinity (see Figure 4.8). The test helps to identify certain species of Enterobacteriaceae, Corynebacterium urealyticum, and Helicobacter pylori.
4. Coagulase test: Coagulase is an enzyme that causes a clot to form when bacteria are incubated with plasma (see Figure 4.8). The test is used to differentiate Staphylococcus aureus (coagulase positive) from coagulase-negative staphylococci.
 الاكثر قراءة في البكتيريا
الاكثر قراءة في البكتيريا
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















