

النبات

مواضيع عامة في علم النبات

الجذور - السيقان - الأوراق

النباتات الوعائية واللاوعائية

البذور (مغطاة البذور - عاريات البذور)

الطحالب

النباتات الطبية


الحيوان

مواضيع عامة في علم الحيوان

علم التشريح

التنوع الإحيائي

البايلوجيا الخلوية


الأحياء المجهرية

البكتيريا

الفطريات

الطفيليات

الفايروسات


علم الأمراض

الاورام

الامراض الوراثية

الامراض المناعية

الامراض المدارية

اضطرابات الدورة الدموية

مواضيع عامة في علم الامراض

الحشرات


التقانة الإحيائية

مواضيع عامة في التقانة الإحيائية


التقنية الحيوية المكروبية

التقنية الحيوية والميكروبات

الفعاليات الحيوية

وراثة الاحياء المجهرية

تصنيف الاحياء المجهرية

الاحياء المجهرية في الطبيعة

أيض الاجهاد

التقنية الحيوية والبيئة

التقنية الحيوية والطب

التقنية الحيوية والزراعة

التقنية الحيوية والصناعة

التقنية الحيوية والطاقة

البحار والطحالب الصغيرة

عزل البروتين

هندسة الجينات


التقنية الحياتية النانوية

مفاهيم التقنية الحيوية النانوية

التراكيب النانوية والمجاهر المستخدمة في رؤيتها

تصنيع وتخليق المواد النانوية

تطبيقات التقنية النانوية والحيوية النانوية

الرقائق والمتحسسات الحيوية

المصفوفات المجهرية وحاسوب الدنا

اللقاحات

البيئة والتلوث


علم الأجنة

اعضاء التكاثر وتشكل الاعراس

الاخصاب

التشطر

العصيبة وتشكل الجسيدات

تشكل اللواحق الجنينية

تكون المعيدة وظهور الطبقات الجنينية

مقدمة لعلم الاجنة


الأحياء الجزيئي

مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي


علم وظائف الأعضاء


الغدد

مواضيع عامة في الغدد

الغدد الصم و هرموناتها

الجسم تحت السريري

الغدة النخامية

الغدة الكظرية

الغدة التناسلية

الغدة الدرقية والجار الدرقية

الغدة البنكرياسية

الغدة الصنوبرية

مواضيع عامة في علم وظائف الاعضاء

الخلية الحيوانية

الجهاز العصبي

أعضاء الحس

الجهاز العضلي

السوائل الجسمية

الجهاز الدوري والليمف

الجهاز التنفسي

الجهاز الهضمي

الجهاز البولي


المضادات الميكروبية

مواضيع عامة في المضادات الميكروبية

مضادات البكتيريا

مضادات الفطريات

مضادات الطفيليات

مضادات الفايروسات

علم الخلية

الوراثة

الأحياء العامة

المناعة

التحليلات المرضية

الكيمياء الحيوية

مواضيع متنوعة أخرى

الانزيمات
Metabolic Changes of Type 1 Diabetes
المؤلف:
Denise R. Ferrier
المصدر:
Lippincott Illustrated Reviews: Biochemistry
الجزء والصفحة:
26-11-2021
1358
Metabolic Changes of Type 1 Diabetes
The metabolic abnormalities of T1D result from a deficiency of insulin that profoundly affects metabolism in three tissues: liver, skeletal muscle, and white adipose (Fig. 1).
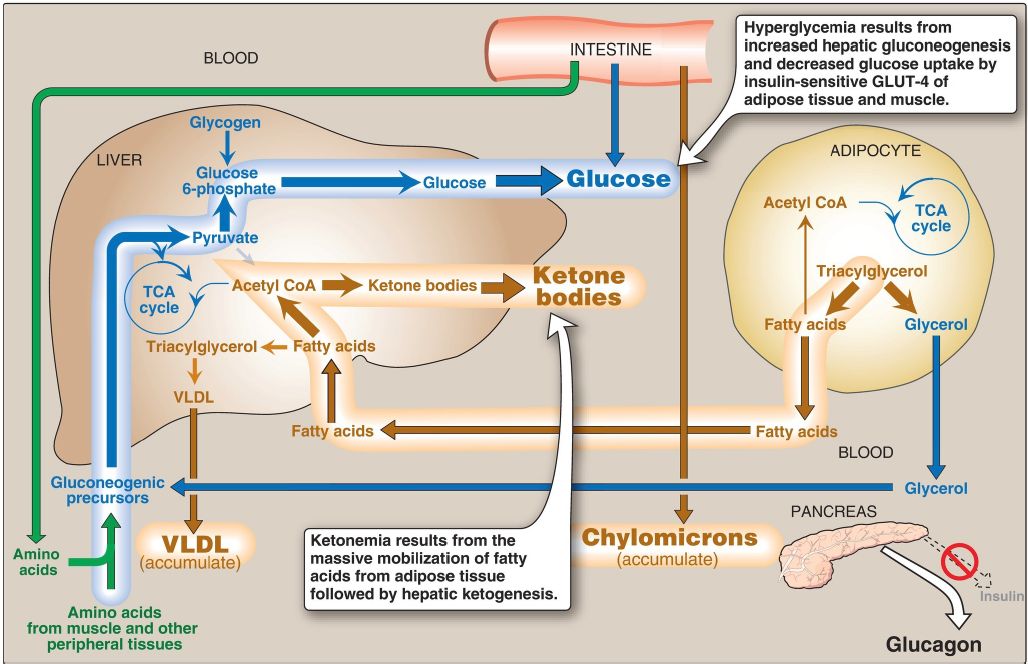
Figure 1: Intertissue relationships in type 1 diabetes. TCA = tricarboxylic acid; CoA = coenzyme A; VLDL = very-low-density lipoproteins; GLUT = glucose transporter.
1. Hyperglycemia and ketonemia: Elevated levels of blood glucose and ketone bodies are the hallmarks of untreated T1D (see Fig. 1).
Hyperglycemia is caused by increased hepatic production of glucose via gluconeogenesis, combined with diminished peripheral utilization (muscle and adipose tissue have the insulin-regulated glucose transporter GLUT-4). Ketonemia results from increased mobilization of fatty acids (FA) from triacylglycerol (TAG) in adipose tissue, combined with accelerated hepatic FA β-oxidation and synthesis of 3-hydroxybutyrate and acetoacetate (ketone bodies). [Note: Acetyl coenzyme A from β-oxidation is the substrate for ketogenesis and the allosteric activator of pyruvate carboxylase, a gluconeogenic enzyme.] Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), a type of metabolic acidosis caused by an imbalance between ketone body production and use, occurs in 25%–40% of those newly diagnosed with T1D and may recur if the patient becomes ill (most commonly with an infection) or does not comply with therapy. DKA is treated by replacing fluid and electrolytes and administering short-acting insulin to gradually correct hyperglycemia without precipitating hypoglycemia.
2. Hypertriacylglycerolemia: Not all of the FA flooding the liver can be disposed of through oxidation and ketone body synthesis. These excess FA are converted to TAG, which are packaged and secreted in very-lowdensity lipoproteins ([VLDL] ). Chylomicrons rich in dietary TAG are secreted by the intestinal mucosal cells following a meal . Because lipoprotein TAG degradation catalyzed by lipoprotein lipase in the capillary beds of adipose tissue is low in diabetes (synthesis of the enzyme is decreased when insulin levels are low), the plasma chylomicron and VLDL levels are elevated, resulting in hypertriacylglycerolemia .
 الاكثر قراءة في الكيمياء الحيوية
الاكثر قراءة في الكيمياء الحيوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















