
Brain in Fasting
 المؤلف:
Denise R. Ferrier
المؤلف:
Denise R. Ferrier
 المصدر:
Lippincott Illustrated Reviews: Biochemistry
المصدر:
Lippincott Illustrated Reviews: Biochemistry
 الجزء والصفحة:
الجزء والصفحة:
 25-11-2021
25-11-2021
 1935
1935
Brain in Fasting
During the early days of fasting, the brain continues to use only glucose as a fuel (Fig. 1, ). Blood glucose is maintained by hepatic gluconeogenesis from glucogenic precursors, such as amino acids from proteolysis and glycerol from lipolysis. In prolonged fasting (beyond 2–3 weeks), plasma ketone bodies reach significantly elevated levels and replace glucose as the primary fuel for the brain (see Figs. 1, and 2). This reduces the need for protein catabolism for gluconeogenesis: Ketone bodies spare glucose and, thus, muscle protein. [Note: As the duration of a fast extends from overnight to days to weeks, blood glucose levels initially drop and then are maintained at the lower level (65–70 mg/dl).]
The metabolic changes that occur during fasting insure that all tissues have an adequate supply of fuel molecules. The response of the major tissues involved in energy metabolism during fasting is summarized in Figure 3.

Figure 1: Major metabolic pathways in the brain during fasting. [Note: The numbers in the circles, which appear both in the figure and in the corresponding citation in the text, indicate important pathways for metabolism of fat or carbohydrates.] CoA = coenzyme A; TCA = tricarboxylic acid; P = phosphate.

Figure 2: Fuel sources used by the brain to meet energy needs in the well-fed
and starved states.
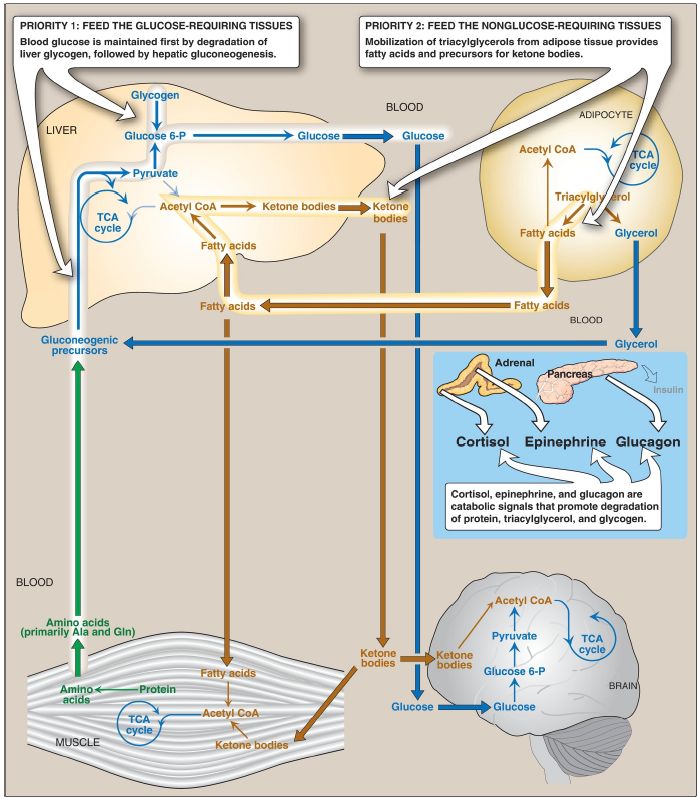
Figure 3: Intertissue relationships during fasting and the hormonal signals
that promote them. P = phosphate; TCA = tricarboxylic acid; CoA = coenzyme
A; Ala = alanine; Gln = glutamine.
 الاكثر قراءة في الكيمياء الحيوية
الاكثر قراءة في الكيمياء الحيوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


