
Amino Acid Metabolism
 المؤلف:
Denise R. Ferrier
المؤلف:
Denise R. Ferrier
 المصدر:
Lippincott Illustrated Reviews: Biochemistry
المصدر:
Lippincott Illustrated Reviews: Biochemistry
 الجزء والصفحة:
الجزء والصفحة:
 12-11-2021
12-11-2021
 2007
2007
Amino Acid Metabolism
Amino acids whose catabolism yields pyruvate or an intermediate of the tricarboxylic acid cycle are termed glucogenic (Fig. 1). They can give rise to the net formation of glucose in the liver and kidneys. The solely glucogenic amino acids are glutamine, glutamate, proline, arginine, histidine, alanine, serine, glycine, cysteine, methionine, valine, threonine, aspartate, and asparagine.
Amino acids whose catabolism yields either acetoacetate or one of its precursors, acetyl coenzyme A (CoA) or acetoacetyl CoA, are termed ketogenic. Leucine and lysine are solely ketogenic. Tyrosine, phenylalanine, tryptophan, and isoleucine are both ketogenic and glucogenic. Nonessential amino acids can be synthesized from metabolic intermediates or from the carbon skeletons of essential amino acids. Essential amino acids need to be obtained from the diet. They include histidine, methionine, threonine, valine, isoleucine, phenylalanine, tryptophan, leucine, and lysine. Phenylketonuria (PKU) is caused by a deficiency of phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH), which converts phenylalanine to tyrosine. Hyperphenylalaninemia may also be caused by deficiencies in the enzymes that synthesize or regenerate the coenzyme for PAH, tetrahydrobiopterin. Untreated individuals with PKU suffer from severe intellectual disability, developmental delay, microcephaly, seizures, and a characteristic musty (mousy) smell of the urine.
Treatment involves controlling dietary phenylalanine. Tyrosine becomes an essential dietary component for people with PKU. Maple syrup urine disease (MSUD) is caused by a partial or complete deficiency in branched-chain a-keto acid dehydrogenase, the enzyme that decarboxylates the branched-chain amino acids (BCAA) leucine, isoleucine, and valine. Symptoms include feeding problems, vomiting, ketoacidosis, changes in muscle tone, and a characteristic sweet smell of the urine. If untreated, the disease leads to neurologic problems that result in death. Treatment involves controlling BCAA intake. Other important genetic diseases associated with amino acid metabolism include albinism, homocystinuria, methylmalonic acidemia, alkaptonuria, histidinemia, tyrosinemia, and cystathioninuria.
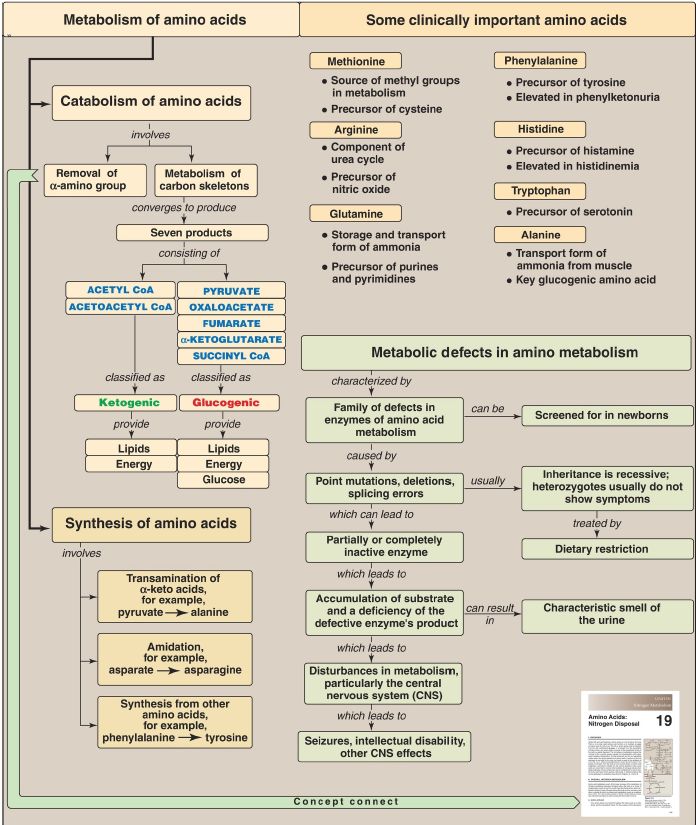
Figure 1: Key concept map for amino acid metabolism. CoA = coenzyme A.
 الاكثر قراءة في الكيمياء الحيوية
الاكثر قراءة في الكيمياء الحيوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


