
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
The bridge rectifier
المؤلف:
Stan Gibilisco
المصدر:
Teach Yourself Electricity and Electronics
الجزء والصفحة:
388
8-5-2021
2908
The bridge rectifier
Another way to get full-wave rectification is the bridge rectifier. It is diagrammed in Fig. 1. The output waveform is just like that of the full-wave, center-tap circuit. The average dc output voltage in the bridge circuit is 90 percent of the rms ac input voltage, just as is the case with center-tap rectification. The PIV across the diodes is 1.4 times the rms ac input voltage. Therefore, each diode needs to have a PIV rating of at least 2.1 times the rms ac input voltage.
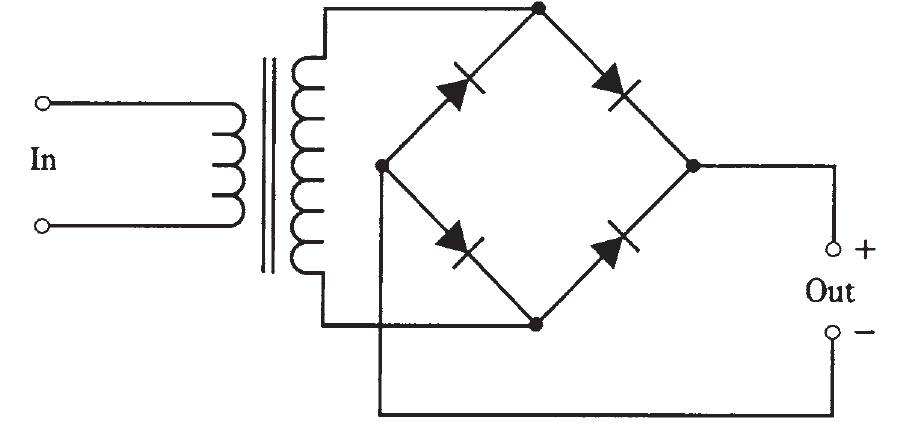
Fig. 1: Schematic diagram of a full-wave bridge rectifier.
The bridge circuit does not need a center-tapped transformer secondary. This is its main practical advantage. Electrically, the bridge circuit uses the entire secondary on both halves of the wave cycle; the center-tap circuit uses one side of the secondary for one half of the cycle, and the other side for the other half of the cycle. For this reason, the bridge circuit makes more efficient use of the transformer.
The main disadvantage of the bridge circuit is that it needs four diodes rather than two. This doesn’t always amount to much in terms of cost, but it can be important when a power supply must deliver a high current. Then, the extra diodes—two for each half of the cycle, rather than one—dissipate more overall heat energy. When current is used up as heat, it can’t go to the load. Therefore, center-tap circuits are preferable in high-current applications.
 الاكثر قراءة في الألكترونيات
الاكثر قراءة في الألكترونيات
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















