Abstract Nouns
What are abstract nouns? You probably can recall that nouns are words that name people, animals, places, things, and ideas. Here, we’ll define abstract nouns, provide abstract noun examples, and give you the information you need for using an abstract noun to write interesting sentences.
What are Abstract Nouns
Abstract nouns are words that name things that are not concrete. Your five physical senses cannot detect an abstract noun – you can’t see it, smell it, taste it, hear it, or touch it. In essence, an abstract noun is a quality, a concept, an idea, or maybe even an event.
Abstract nouns and concrete nouns are usually defined in terms of one another. Something that is abstract exists only in the mind, while something that is concrete can be interacted with in a physical way. Qualities, relationships, theories, conditions, and states of being are some examples of the types of things abstract nouns define.
Types of Abstract Nouns
It’s not always easy to determine if a noun is abstract or concrete. Many grammar experts argue over whether certain terms, making things even worse. The line separating abstract nouns from concrete nouns is often quite blurry. For example, many abstract noun lists include the word laughter, but others leave it out, as it’s something that can be heard, seen, and physically felt.
Abstract Noun Examples
The following lists contain different types of abstract nouns. Certain abstract nouns, especially the ones describing feelings and emotions, easily fit into multiple categories, as they can be used in different ways. Get to know them, and it’ll be easier for you to spot an abstract noun when you see one.
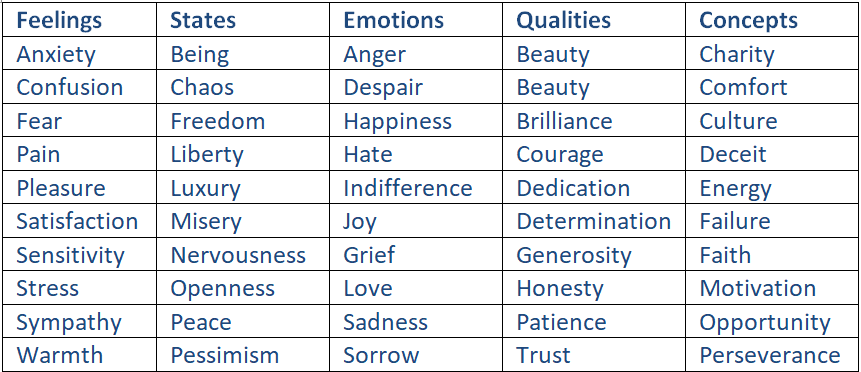
Although you may not realize it, you experience abstract nouns every day and in many different types of situations. Once you’ve read these abstract noun examples, you’ll probably find it very easy to come up with some abstract nouns of your own.
More Examples
• Love, fear, anger, joy, excitement, and other emotions are abstract nouns.
• Courage, bravery, cowardice, and other such states are abstract nouns.
• Desire, creativity, uncertainty, and other innate feelings are abstract nouns.
These are just a few examples of non-concrete words that are sensed. The following sentences contain abstract noun examples which have been italicized for easy identification. Notice that although the ideas expressed are real, they are things you can’t see, touch, taste, smell, or hear.
• I want to see justice served.
• I’d like the freedom to travel all over the world.
• Joe felt a nagging sense of doom.
• Love is a kind of irresistible desire; it’s hard to define.
• When Sarah jumped into the lake to rescue a drowning cat, her bravery astonished onlookers.
 الاكثر قراءة في Abstract nouns
الاكثر قراءة في Abstract nouns
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


