
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
FM Modulation
المؤلف:
Walter Koechner Michael Bass
المصدر:
Solid-state Lasers
الجزء والصفحة:
325
22-1-2021
1584
FM Modulation
Light passing through an electro-optic phase modulator will be up- or downshifted in frequency unless it passes through at the time when the intracavity phase modulator δ(t) is stationary at either of its extrema. The recirculating energy passing through the phase modulator at any other time receives a Doppler shift proportional to dδ/dt, and the repeated Doppler shifts on successive passes through the modulator eventually push this energy outside the frequency band over which gain is available from the laser medium. The interaction of the spectrally widened circulating power with the narrow laser linewidth leads to a reduction in gain for most frequency components. Thus, the effect of the phase modulator is similar to the loss modulator, and the previous discussion of loss modulation also applies here. The existence of two phase extrema per period creates a phase uncertainty in the mode-locked pulse position since the pulse can occur at either of two equally probable phases relative to the modulating signal. The quadratic variation of δ(t) about the pulse arrival time also produces a frequency “chirp” within the short mode-locked pulses.
In the FM case, the internal FM introduces a sinusoidally varying phase perturbation such that the round-trip transmission through the modulator is given approximately by
 ........(1)
........(1)
where δFM is the peak phase retardation through the modulator. The ± sign corresponds to the two possible phase positions at which the pulse can pass through the modulator, as mentioned earlier. With these parameters the pulse width of phase mode-locked pulses is given by
 ........(2)
........(2)
The time-bandwidth product is given by
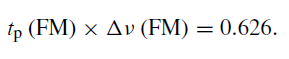 ........(3)
........(3)
In an electro-optic phase modulator the phase retardation is proportional to the modulating voltage, hence δFM ∝ P1/2in , where Pin is the drive power into the modulator. Therefore, we obtain from (2) the following expression for the pulse width: tp(FM) ∝ P−1/8in , which indicates that the pulses shorten very slowly with increased modulator drive. More effective in shortening the pulses is an increase of the modulation frequency. Since νm = c/2L, the pulse width will be proportional to the square root of the cavity length.
In order to calculate the pulse width from (2), we can calculate the saturated gain coefficient g by equating the loop gain with the loss in the resonator
 .......(4)
.......(4)
where R is the effective reflectivity of the output mirror and includes all losses.
For a typical Nd :YAG laser with 10% round-trip loss, that is, R = 0.9, a resonator length of 60 cm, and a linewidth of 120 GHz, the pulse length is given by tp(FM) = 39(1/δFM)1/4. For δFM = 1 rad, which is easily obtainable, pulses of 39 ps can be generated.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الليزر
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الليزر
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















