
Thermal Management
 المؤلف:
Walter Koechner, Michael Bass
المؤلف:
Walter Koechner, Michael Bass
 المصدر:
Solid-State Lasers
المصدر:
Solid-State Lasers
 الجزء والصفحة:
212
الجزء والصفحة:
212
 20-1-2021
20-1-2021
 1437
1437
Thermal Management
Diode-array pumping offers dramatic improvements in efficiency of solid-state laser systems. However, the need to maintain the operating temperature within a relatively narrow range requires a more elaborate thermal management system as compared to flashlamp-pumped lasers.
In end-pumped systems, the diode wavelength is usually temperature tuned to the peak absorption line of the laser and maintained at that wavelength by controlling the array temperature with a thermoelectric cooler. This approach works well for small lasers, and systems including thermoelectric coolers can work over a large range of ambient temperatures.
In large systems, the power consumption of thermoelectric coolers is usually prohibitive. For these systems, a liquid cooling loop with a refrigeration stage can be employed that maintains the temperature of the coolant independent of the environment. However, the coefficient of performance for refrigerators is typically no greater than one. Therefore, the electrical input power requirement is equal to the heat load to be controlled.
Recently, the development of diode arrays which can operate at high junction temperatures has eliminated the need for refrigerated cooling loops for special cases such as military systems. Diode arrays have been operated at junction temperatures as high as 75◦ C, which is higher than ambient in most situations. A simple liquid-to-air cooling system provides the most efficient thermal control system for the laser because only the power consumption of a pump and possibly a fan is added to the total electrical requirements.
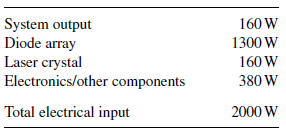
The power dissipation of the various subsystems of a pulsed diode-pumped laser is listed in Table 1. The system has a repetition rate of 200 Hz and an output pulse energy of 0.8 J/pulse. By far the greatest heat dissipation occurs in the diode pump arrays, and accounts for approximately 65% of the system input power. The solid-state laser medium itself dissipates heat at a rate approximately equal to the output power from the laser system. The electronics dissipate on the order of 19% of the input power.
TABLE 1. Power dissipation from a diode-array-pumped solid-state laser.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الليزر
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الليزر
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


