

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
First-Order Reactions
المؤلف:
University of Missouri System
المصدر:
Introductory chemistry
الجزء والصفحة:
.................
18-12-2020
5647
First-Order Reactions
We have seen earlier that the rate law of a generic first-order reaction where A → B can be expressed in terms of the reactant concentration:
Rate of reaction = – [latex] frac{Delta [A]}{Delta t} [/latex] = [latex] extit{k}[A]{}^{1} [/latex]
This form of the rate law is sometimes referred to as the differential rate law. We can perform a mathematical procedure known as an integration to transform the rate law to another useful form known as the integrated rate law:
ln [latex] frac{{[A]}_t}{{[A]}_0} [/latex]= –[latex] extit{k}t [/latex]
where “ln” is the natural logarithm, [A]0 is the initial concentration of A, and [A]t is the concentration of A at another time.
The process of integration is beyond the scope of this textbook, but is covered in most calculus textbooks and courses. The most useful aspect of the integrated rate law is that it can be rearranged to have the general form of a straight line (y = mx + b).
ln [latex] {[A]}_t [/latex]= –[latex] extit{k}t + ln {[A]}_0 [/latex]
(y = mx + b)
Therefore, if we were to graph the natural logarithm of the concentration of a reactant (ln) versus time, a reaction that has a first-order rate law will yield a straight line, while a reaction with any other order will not yield a straight line (Figure 17.7 “Concentration vs. Time, First-Order Reaction”). The slope of the straight line corresponds to the negative rate constant, –k, and the y-intercept corresponds to the natural logarithm of the initial concentration.
Figure 17.7. Concentration vs. Time, First-Order Reaction
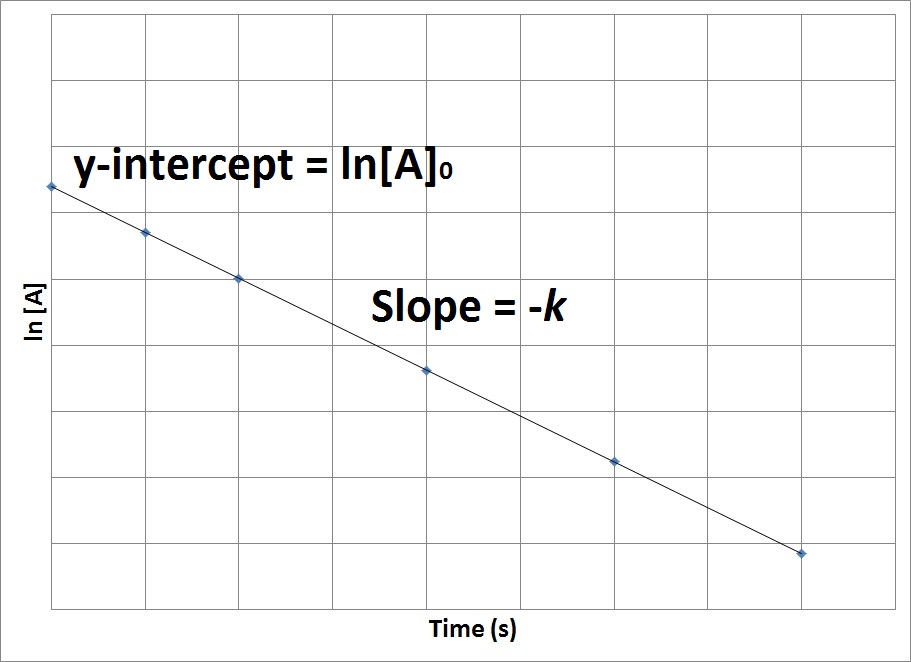
This graph shows the plot of the natural logarithm of concentration versus time for a first-order reaction.
Example 4
The decomposition of a pollutant in water at 15oC occurs with a rate constant of 2.39 y-1, following first-order kinetics. If a local factory spills 6,500 moles of this pollutant into a lake with a volume of 2,500 L, what will the concentration of pollutant be after two years, assuming the lake temperature remains constant at 15oC?
Solution
We are given the rate constant and time and can determine an initial concentration from the number of moles and volume given.
[latex] {[Pollutant]}_0 [/latex]= [latex] frac{{ m 6500 mol}}{{ m 2500 L}} [/latex] = 2.6 M
We can substitute this data into the integrated rate law of a first-order equation and solve for the concentration after 2.0 years:
ln [latex] {[Pollutant]}_{2 y} [/latex]= –[latex] extit{k}t + ln {[Pollutant]}_0 [/latex]
ln [latex] {[Pollutant]}_{2 y} [/latex]= –[latex] (2.39 y {}^{-1}) (2.0 y) + ln (2.6 M) [/latex]
ln [latex] {[Pollutant]}_{2 y} [/latex]= –[latex] 4.78 + 0.955 = -3.82 [/latex]
[latex] {[Pollutant]}_{2 y} [/latex]= [latex] e{}^{-3.82} = 0.022 M [/latex]
 الاكثر قراءة في حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية
الاكثر قراءة في حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















