

النبات

مواضيع عامة في علم النبات

الجذور - السيقان - الأوراق

النباتات الوعائية واللاوعائية

البذور (مغطاة البذور - عاريات البذور)

الطحالب

النباتات الطبية


الحيوان

مواضيع عامة في علم الحيوان

علم التشريح

التنوع الإحيائي

البايلوجيا الخلوية


الأحياء المجهرية

البكتيريا

الفطريات

الطفيليات

الفايروسات


علم الأمراض

الاورام

الامراض الوراثية

الامراض المناعية

الامراض المدارية

اضطرابات الدورة الدموية

مواضيع عامة في علم الامراض

الحشرات


التقانة الإحيائية

مواضيع عامة في التقانة الإحيائية


التقنية الحيوية المكروبية

التقنية الحيوية والميكروبات

الفعاليات الحيوية

وراثة الاحياء المجهرية

تصنيف الاحياء المجهرية

الاحياء المجهرية في الطبيعة

أيض الاجهاد

التقنية الحيوية والبيئة

التقنية الحيوية والطب

التقنية الحيوية والزراعة

التقنية الحيوية والصناعة

التقنية الحيوية والطاقة

البحار والطحالب الصغيرة

عزل البروتين

هندسة الجينات


التقنية الحياتية النانوية

مفاهيم التقنية الحيوية النانوية

التراكيب النانوية والمجاهر المستخدمة في رؤيتها

تصنيع وتخليق المواد النانوية

تطبيقات التقنية النانوية والحيوية النانوية

الرقائق والمتحسسات الحيوية

المصفوفات المجهرية وحاسوب الدنا

اللقاحات

البيئة والتلوث


علم الأجنة

اعضاء التكاثر وتشكل الاعراس

الاخصاب

التشطر

العصيبة وتشكل الجسيدات

تشكل اللواحق الجنينية

تكون المعيدة وظهور الطبقات الجنينية

مقدمة لعلم الاجنة


الأحياء الجزيئي

مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي


علم وظائف الأعضاء


الغدد

مواضيع عامة في الغدد

الغدد الصم و هرموناتها

الجسم تحت السريري

الغدة النخامية

الغدة الكظرية

الغدة التناسلية

الغدة الدرقية والجار الدرقية

الغدة البنكرياسية

الغدة الصنوبرية

مواضيع عامة في علم وظائف الاعضاء

الخلية الحيوانية

الجهاز العصبي

أعضاء الحس

الجهاز العضلي

السوائل الجسمية

الجهاز الدوري والليمف

الجهاز التنفسي

الجهاز الهضمي

الجهاز البولي


المضادات الميكروبية

مواضيع عامة في المضادات الميكروبية

مضادات البكتيريا

مضادات الفطريات

مضادات الطفيليات

مضادات الفايروسات

علم الخلية

الوراثة

الأحياء العامة

المناعة

التحليلات المرضية

الكيمياء الحيوية

مواضيع متنوعة أخرى

الانزيمات
Applications of Transgenic Technologies
المؤلف:
Genetics Home Reference
المصدر:
Molecular Biology and Biotechnology 5th Edition
الجزء والصفحة:
11-12-2020
1575
Applications of Transgenic Technologies
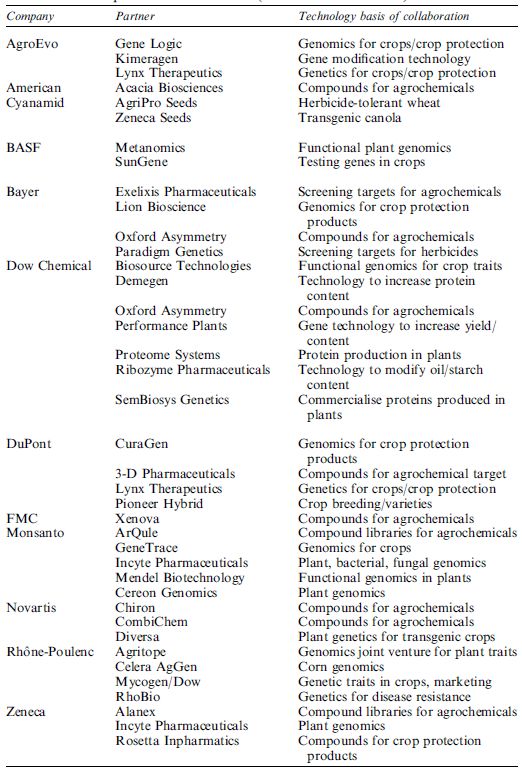
The application of transgenic technologies in plant biotechnology has the potential to exceed the technical advances that have taken place in previous ‘revolutions’ in production agriculture. It has only taken years of commercial growth of transgenic crops in North America for 52% of the soybean, 30% of the maize and 9% of both cotton and canola grown in 1999 to be transgenic, with increasing production of a wide range of other transgenic crops such as rice, wheat, barley, sorghum, sugar cane, sugar beet, tomato, potato, sunflower, peanut, papaya, tree species and horticultural crops such as carnations. Major companies involved in commercialisation of transgenic crops and their alliances are given in Table .
Of the 69.5 million acres of transgenic crops grown (27.8 million hectares) in 1998, 74% were in the USA, 15% in Argentina, 10% in Canada and 1% in Australia. The transgenic traits grown commercially were dominated by herbicide tolerance (71%) and insect resistance (28%), with only 1% for the other traits. However, the transgenic plants currently being commercialised are the first generation of transgenic crops and three generations of transgenic
Table . Major companies involved in commercialisation of transgenic crops and their alliances .
crops can be envisaged:
- First generation – production traits (e.g. herbicide tolerance, insect/ disease resistance).
- Second generation – stacked genes for multiple traits (e.g. combinations of disease resistance genes plus quality traits).
- Third generation – varieties tailored for specific end uses (e.g. food, fibre, fuel, lubricants, plastics, pharmaceuticals and raw materials for industrial processes).
Already, the production of second-generation transgenic crops is in progress and some specific examples of applications are given in the following sections. However, to achieve the potential benefits of transgenic plant biotechnology, there are many additional factors to consider, which include regulation of biotechnology, intellectual property, food safety, public acceptance, allergenicity, labelling, choice, the environment,segregation of transgenic products and international trade.
The emphasis here is on application and potential benefits of transgenic technologies. As in any developing technologies, the aim is to maximize the benefits and minimize the risks.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في التقانة الإحيائية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في التقانة الإحيائية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















