
Equatorial mountings: The coud´e system
 المؤلف:
A. Roy, D. Clarke
المؤلف:
A. Roy, D. Clarke
 المصدر:
Astronomy - Principles and Practice 4th ed
المصدر:
Astronomy - Principles and Practice 4th ed
 الجزء والصفحة:
p 377
الجزء والصفحة:
p 377
 1-9-2020
1-9-2020
 2438
2438
Equatorial mountings: The coud´e system
In the case of some types of measurement, the analysing equipment is too cumbersome and heavy for attachment at the focal plane of the telescope, especially when the telescope needs to be oriented over a large range of positions. Such an instrument might be a spectrometer with a small RLD with a large camera. One way around this problem is to arrange the optical system of the telescope to provide an image at a fixed position in space, independent of the telescope’s orientation, and to fix permanently the analysing equipment so that it accepts the energy contained in the image. The design of the equatorial mounting lends itself to such an optical system, whereby the converging light rays are directed along or through the polar axis. The system is known as a coud´e telescope and an example of this system is illustrated in figure 1. It consists of a design similar to the Cassegrain but an extra flat mirror is placed with its reflecting surface on the declination axis so that the light is made to pass along the polar axis. The flat mirror is mechanically mounted to the telescope so that it rotates at half the rate of the telescope around the declination axis. As the reflection efficiency of a mirror depends on the angle of incidence of the incoming light, the transmission efficiency of the coud´e system will depend slightly on the declination of the object which is observed. A coud´e telescope has a high focal ratio, usually in the range f/30– f/60.
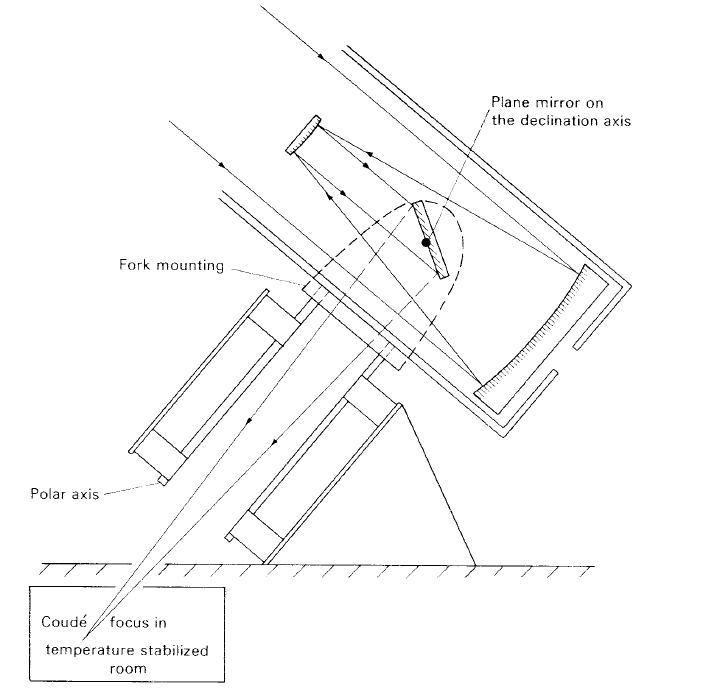
Figure 1. The coud´e telescope.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


