
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
Bolometric magnitudes
المؤلف:
A. Roy, D. Clarke
المصدر:
Astronomy - Principles and Practice 4th ed
الجزء والصفحة:
p 310
27-8-2020
1929
Bolometric magnitudes
When the properties of stars are being compared, it is advantageous to use a magnitude system which is independent of any particular detector system with its associated wavelength-selective property. It is useful to be able to know the brightness or magnitude of stars as they would be determined by a system which is equally sensitive to all wavelengths. For this purpose, a system known as the bolometric magnitude scale is frequently used. From a knowledge of the energy envelope of a star and the spectral response curve of the selective detector, it is possible to perform calculations so that the total amount of energy available for measurement by a bolometer can be predicted. In principle, any magnitude determination by a particular system can be converted to a bolometricmagnitude (mbol) by the appropriate correction, known as the bolometric correction (BC). Thus, in general,
mbol = m + BC
and, therefore,
BC = mbol − m. (1)
Consider the bolometric correction in relation to the visual magnitude scale. namely
m = k − 2·5 log10 B
Table 1. Bolometric corrections to V band magnitudes.
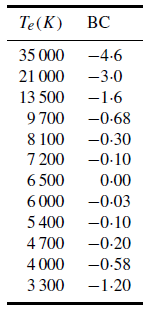
the bolometric magnitude scale can be represented as
mbol = kbol − 2·5 log10 Bbol. (2)
Similarly, the visual band scale can be represented as
mV = V = kV − 2·5 log10 BV . (3)
In equation (2), kbol is an arbitrary constant while kV in equation (3) has been chosen according to some suitable standard stars. Subtraction of equation (3) from (2) gives
mbol − mV = BC = kbol − kV − 2·5 log10 (Bbol/BV)(4)
The ratio Bbol/BV has a minimum value for a star with a temperature providing the maximum in its energy envelope at the same wavelength as the peak sensitivity of the selective detector. For the V -band system, this occurs when the temperature is close to 6500 K. The value of kbol is chosen so that the bolometric correction is zero for this temperature. Since Bbol/BV has a minimum value at this temperature, it is easy to demonstrate, using equation (4), that the bolometric correction is negative for stars with temperatures on either side of 6500 K. The bolometric corrections to V -band magnitudes are listed in table 1.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















