
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
Effect of the Earth’s shape on a satellite orbit
المؤلف:
A. Roy, D. Clarke
المصدر:
Astronomy - Principles and Practice 4th ed
الجزء والصفحة:
p 194
14-8-2020
1962
Effect of the Earth’s shape on a satellite orbit
The Earth is not a perfect sphere. Even before the days of artificial satellites, it was known that the diameter of the Earth, measured from pole to pole, was about 43 km less than an equatorial diameter. Newton explained this equatorial bulge of matter as being a consequence of the Earth’s rapid rotation. The departure of the Earth from a sphere, therefore, acts gravitationally as a disturbing force on the satellite. Indeed, it acts upon the Moon itself, producing perturbations in its orbit.
Many artificial satellites are so close to the Earth that other departures of the Earth’s shape from a sphere produce observable changes in the satellite orbits. By predicting the types of orbital change due to particular departures and then observing them, our knowledge of the Earth’s figure, as it is called, has increased enormously. For example, the equator is found to be elliptical rather than circular, the difference between longest and shortest equatorial diameters being about half a kilometre. The northern hemisphere is slightly sharper than the southern hemisphere, imparting a ‘pear-shaped’ aspect to our planet. The order of magnitude of this difference is only about 20 m. Other, even smaller, features of the Earth’s figure have been measured.
The effects upon a satellite orbit due to these causes are best described by the changes that take place in the orbital elements. The semi-major axis, eccentricity and inclination of the orbital plane suffer purely periodic changes. This means that the Earth’s departure from a sphere has no disastrous
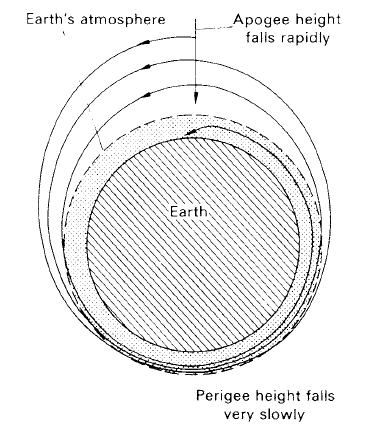
Figure 1. The evolution of a satellite’s orbit due to atmospheric drag.
effects upon the satellite; it will neither spiral in to be burned up in the Earth’s atmosphere nor recede indefinitely to be lost in interplanetary space.
The other three elements are the right ascension of the ascending node (since the equator in the case of an artificial Earth satellite is the most useful reference plane), the argument of perigee (again measured along the orbital plane from ascending node to the point in the orbit nearest the central body—in this case the Earth) and the time of perigee passage. All three suffer secular as well as periodic changes.
Thus, the ascending node precesses slowly backwards, at a few degrees per day for typical satellites, so that a revolution of the orbital plane takes some months in contrast to the satellite’s own period of revolution about the Earth of an hour or two. It is also found that if the inclination is less than 63◦ 26', the orbit rotates slowly in the direction in which the satellite moves but precesses backwards within the plane, like the plane itself, if the inclination is greater than 63◦ 26'.
Since a world-wide network of tracking stations keeps constant watch on many satellites, these secular rates, caused by the Earth’s departure from a sphere, can be measured accurately. In turn, through the formulas relating these rates to parameters describing the Earth’s figure, the mathematical description of the planet’s shape can be evaluated
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















