

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
The Carbonyl Group
المؤلف:
..................
المصدر:
LibreTexts Project
الجزء والصفحة:
.................
9-7-2019
1932
The Carbonyl Group
C=O is prone to additions and nucleophillic attack because or carbon's positive charge and oxygen's negative charge. The resonance of the carbon partial positive charge allows the negative charge on the nucleophile to attack the Carbonyl group and become a part of the structure and a positive charge (usually a proton hydrogen) attacks the oxygen. Just a reminder, the nucleophile is a good acid therefore "likes protons" so it will attack the side with a positive charge.
Before we consider in detail the reactivity of aldehydes and ketones, we need to look back and remind ourselves of what the bonding picture looks like in a carbonyl. Carbonyl carbons are sp2 hybridized, with the three sp2 orbitals forming soverlaps with orbitals on the oxygen and on the two carbon or hydrogen atoms. These three bonds adopt trigonal planar geometry. The remaining unhybridized 2p orbital on the central carbonyl carbon is perpendicular to this plane, and forms a ‘side-by-side’ pbond with a 2p orbital on the oxygen.
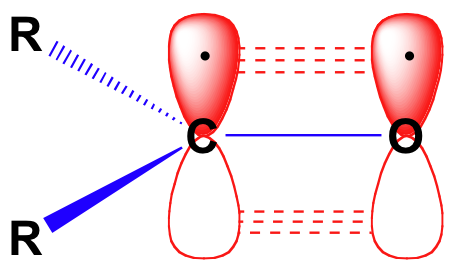
The carbon-oxygen double bond is polar: oxygen is more electronegative than carbon, so electron density is higher on the oxygen side of the bond and lower on the carbon side. Recall that bond polarity can be depicted with a dipole arrow, or by showing the oxygen as holding a partial negative charge and the carbonyl carbon a partial positive charge.

A third way to illustrate the carbon-oxygen dipole is to consider the two main resonance contributors of a carbonyl group: the major form, which is what you typically see drawn in Lewis structures, and a minor but very important contributor in which both electrons in the pbond are localized on the oxygen, giving it a full negative charge. The latter depiction shows the carbon with an empty 2p orbital and a full positive charge.
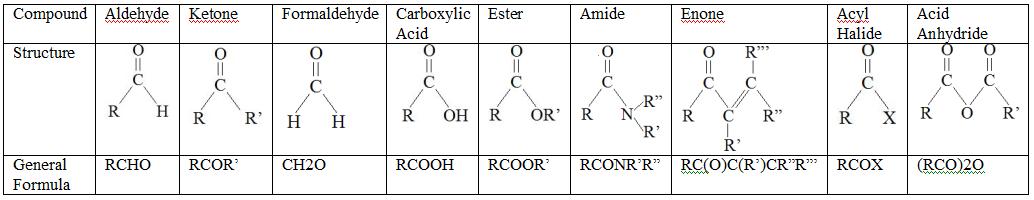
Some Carbonyl Compounds
 الاكثر قراءة في تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية
الاكثر قراءة في تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















