

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Kinds of Organic Reactions
المؤلف:
..................
المصدر:
LibreTexts Project
الجزء والصفحة:
.................
8-7-2019
1179
Kinds of Organic Reactions
If you scan any organic textbook you will encounter what appears to be a very large, often intimidating, number of reactions. These are the "tools" of a chemist, and to use these tools effectively, we must organize them in a sensible manner and look for patterns of reactivity that permit us make plausible predictions. Most of these reactions occur at special sites of reactivity known as functional groups, and these constitute one organizational scheme that helps us catalog and remember reactions.
Ultimately, the best way to achieve proficiency in organic chemistry is to understand how reactions take place, and to recognize the various factors that influence their course.
First, we identify four broad classes of reactions based solely on the structural change occurring in the reactant molecules. This classification does not require knowledge or speculation concerning reaction paths or mechanisms. The four main reaction classes are additions, eliminations, substitutions, and rearrangements.
Addition Reaction
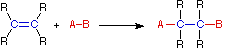
Elimination Reaction
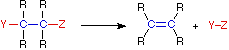
Substitution Reaction
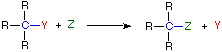
Rearrangement Reaction
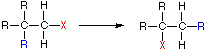
In an addition reaction the number of σ-bonds in the substrate molecule increases, usually at the expense of one or more π-bonds. The reverse is true of elimination reactions, i.e.the number of σ-bonds in the substrate decreases, and new π-bonds are often formed. Substitution reactions, as the name implies, are characterized by replacement of an atom or group (Y) by another atom or group (Z). Aside from these groups, the number of bonds does not change. A rearrangement reaction generates an isomer, and again the number of bonds normally does not change.
The examples illustrated above involve simple alkyl and alkene systems, but these reaction types are general for most functional groups, including those incorporating carbon-oxygen double bonds and carbon-nitrogen double and triple bonds. Some common reactions may actually be a combination of reaction types.
 الاكثر قراءة في تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية
الاكثر قراءة في تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















