

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Using Lewis Dot Symbols to Describe Covalent Bonding
المؤلف:
........
المصدر:
LibreTexts Project
الجزء والصفحة:
............
8-4-2019
2100
Using Lewis Dot Symbols to Describe Covalent Bonding
This sharing of electrons allowing atoms to "stick" together is the basis of covalent bonding. There is some intermediate distant, generally a bit longer than 0.1 nm, or if you prefer 100 pm, at which the attractive forces significantly outweigh the repulsive forces and a bond will be formed if both atoms can achieve a completen s2np6 configuration. It is this behavior that Lewis captured in his octet rule. The valence electron configurations of the constituent atoms of a covalent compound are important factors in determining its structure, stoichiometry, and properties. For example, chlorine, with seven valence electrons, is one electron short of an octet. If two chlorine atoms share their unpaired electrons by making a covalent bond and forming Cl2, they can each complete their valence shell:
Each chlorine atom now has an octet. The electron pair being shared by the atoms is called a bonding pair A pair of electrons in a Lewis structure that is shared by two atoms, thus forming a covalent bond.; the other three pairs of electrons on each chlorine atom are called lone pairsA pair of electrons in a Lewis structure that is not involved in covalent bonding.. Lone pairs are not involved in covalent bonding. If both electrons in a covalent bond come from the same atom, the bond is called a coordinated covalent bondA covalent bond in which both electrons come from the same atom. when we discuss atoms with less than an octet of electrons.
We can illustrate the formation of a water molecule from two hydrogen atoms and an oxygen atom using Lewis dot symbols:
The structure on the right is the Lewis electron structure, or Lewis structure, for H2O. With two bonding pairs and two lone pairs, the oxygen atom has now completed its octet. Moreover, by sharing a bonding pair with oxygen, each hydrogen atom now has a full valence shell of two electrons. Chemists usually indicate a bonding pair by a single line, as shown here for our two examples:
The following procedure can be used to construct Lewis electron structures for more complex molecules and ions:
1. Arrange the atoms to show specific connections. When there is a central atom, it is usually the least electronegative element in the compound. Chemists usually list this central atom first in the chemical formula (as in CCl4 and CO32−, which both have C as the central atom), which is another clue to the compound’s structure. Hydrogen and the halogens are almost always connected to only one other atom, so they are usually terminal rather than central.
 الاكثر قراءة في مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء
الاكثر قراءة في مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية














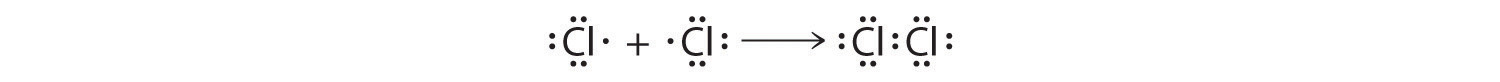
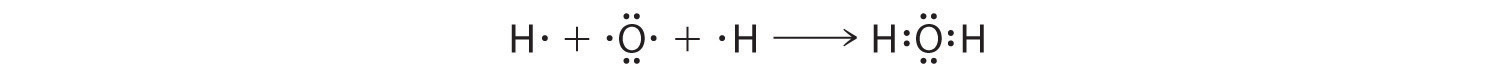


 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















