

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
RNA, a Different Nucleic Acid
المؤلف:
William Reusch
المصدر:
Virtual Textbook of Organic Chemistry
الجزء والصفحة:
............
24-8-2018
2542
RNA, a Different Nucleic Acid
The high molecular weight nucleic acid, DNA, is found chiefly in the nuclei of complex cells, known as eucaryotic cells, or in the nucleoid regions of procaryotic cells, such as bacteria. It is often associated with proteins that help to pack it in a usable fashion.
In contrast, a lower molecular weight, but much more abundant nucleic acid, RNA, is distributed throughout the cell, most commonly in small numerous organelles called ribosomes. Three kinds of RNA are identified, the largest subgroup (85 to 90%) being ribosomal RNA, rRNA, the major component of ribosomes, together with proteins. The size of rRNA molecules varies, but is generally less than a thousandth the size of DNA. The other forms of RNA are messenger RNA , mRNA, and transfer RNA , tRNA. Both have a more transient existence and are smaller than rRNA.
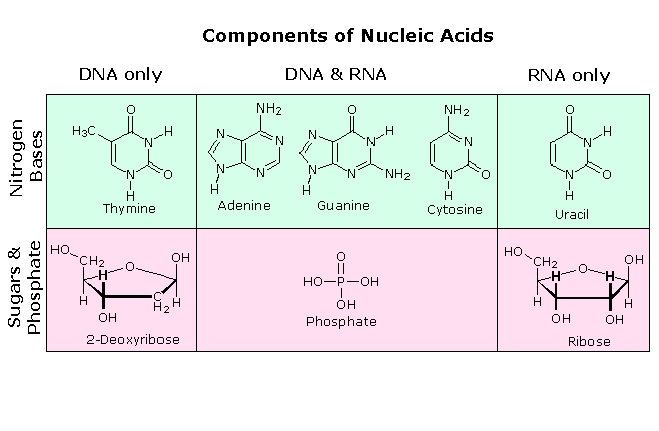
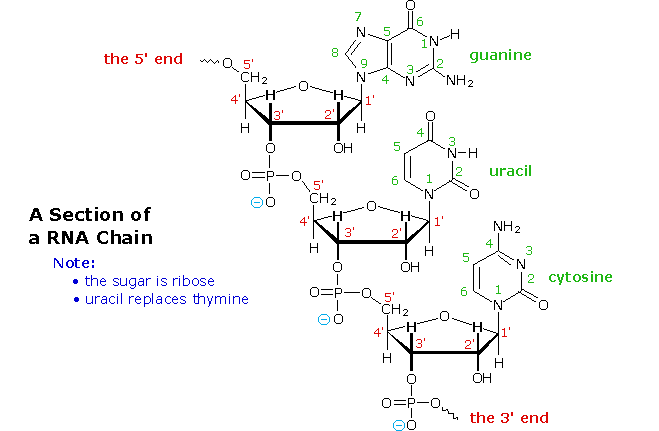
All these RNA's have similar constitutions, and differ from DNA in two important respects. As shown in the following diagram, the sugar component of RNA is ribose, and the pyrimidine base uracil replaces the thymine base of DNA. The RNA's play a vital role in the transfer of information (transcription) from the DNA library to the protein factories called ribosomes, and in the interpretation of that information (translation) for the synthesis of specific polypeptides. These functions will be described later.
 الاكثر قراءة في الاحماض النووية
الاكثر قراءة في الاحماض النووية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















