
Fission of U-235
 المؤلف:
Franklin Potter and Christopher Jargodzki
المؤلف:
Franklin Potter and Christopher Jargodzki
 المصدر:
Mad about Modern Physics
المصدر:
Mad about Modern Physics
 الجزء والصفحة:
p 99
الجزء والصفحة:
p 99
 5-11-2016
5-11-2016
 708
708
Fission of U-235
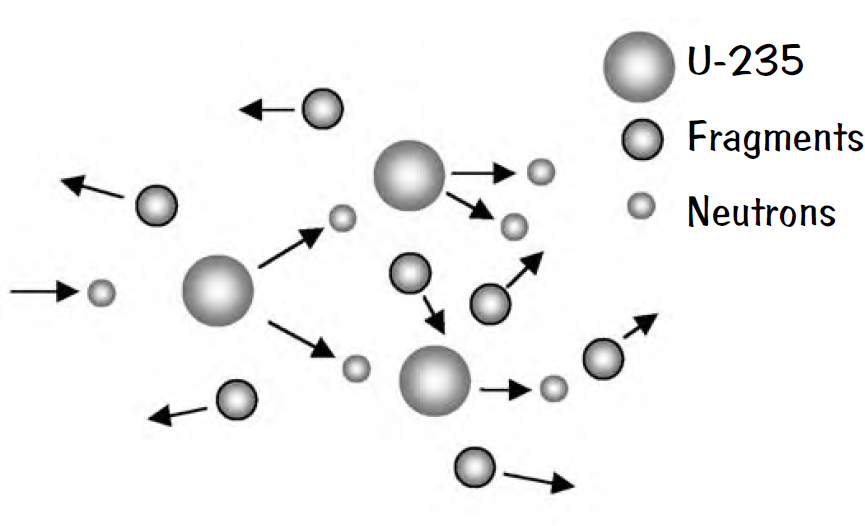
During World War II the Germans and the Allies were both working on projects related to nuclear weapons development. One can calculate the minimum mass of U-235 required for a fission weapon from present-day nuclear physics data sheets. That value is the amount required if the neutrons produced by the fission of U-235 encounter stationary target nuclei. The problem is much more difficult for two important reasons. Can you identify them?
Answer
There are two major problems to be overcome in designing a fission device. The neutron distribution in a pure U-235 solid would decrease as the inverse distance squared from each nuclear decay source, and the target nuclei would be moving away during the expansion, so one has a diffusion problem complicated by moving targets. The moving targets contribute at least two difficulties: the density of targets is rapidly decreasing, and the neutron-capture cross section is a function of neutron kinetic energy as seen from the reference frame riding with each U-235 nucleus. Without the proper neutron capture rate by the receding U-235 nuclei, the chain reaction fizzles out.
Of course, the nuclear device cannot be expected to be pure U-235 because the isolation of enough quantities of U-235 from U-238 is too difficult and too costly. Therefore, there is mostly U-238 in the expanding solid with some U-235, so we have all the previously listed problems to solve but also must account for the nuclear properties of the U-238 as well as the U-235.
 الاكثر قراءة في طرائف الفيزياء
الاكثر قراءة في طرائف الفيزياء
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


