
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
Mass and Energy
المؤلف:
Franklin Potter and Christopher Jargodzki
المصدر:
Mad about Modern Physics
الجزء والصفحة:
p 41
13-10-2016
331
Mass and Energy
A symbol of the twentieth century is the famous Einstein relation between mass and energy. Here are four possible equations: (1) E0 = mc2 (2) E = mc2 (3) E0 = m0c2 (4) E = m0c2. In the equations c is the velocity of light, E is the total energy of a free body, E0 its rest energy, m0 its rest mass, and m its mass.
Which of these equations expresses one of the main consequences of the STR? Which equation was first written by Einstein and was considered by him a consequence of STR?
Answer
The answer to both questions is equation 1, although the majority of physicists seem to prefer equations 2 or 3! Their choices probably are caused by the confusing terminology widely used in the physics literature that says that a body at rest has a “proper mass” or “rest mass” m0, and a body in motion has a “relativistic mass” m = 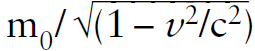 .
.
There is only one mass in physics, m, which does not depend on the reference frame. This mass m is the relativistic invariant quantity in E2 – p2c2 = m2c4, whereas the energy is different in different reference systems. There is no need to place the index 0 with the mass. However, the total energy E needs the 0 index if the particle has no momentum in that reference frame that is, E0 = mc2.
For a complete and stimulating discussion of these ideas and their history see the L. V. Okun reference below.