
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
Light Clock
المؤلف:
Franklin Potter and Christopher Jargodzki
المصدر:
Mad about Modern Physics
الجزء والصفحة:
p 16
3-10-2016
637
Light Clock
Some museums and laboratories have a light clock with two parallel mirrors and a pulse of light bouncing back and forth repeatedly, retracing the same path over and over, keeping very accurate time as each complete transit of the light pulse is detected and counted. The mirror separation is usually about a meter or less, so a very large number of reflections occur during each second of time. Suppose this light clock is moved sideways parallel to the mirrors at a constant velocity, and assume that the light will continue to reflect off both mirrors during this sideward movement. Will the clock continue to keep accurate time?

Answer
Yes and no. The clock will continue to keep accurate time in both reference frames, in the laboratory frame, and in the rest frame of the clock. But the tick rates will be different. In the frame moving with the clock, the light flashes follow the same path as before, reflecting perpendicularly to each mirror, keeping the same tick rate.
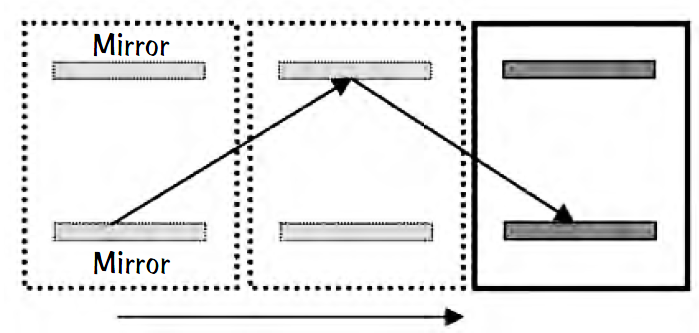
In the laboratory frame, the light continues to reflect off each mirror repeatedly, but during transit from one mirror to the other the path length is longer, being the diagonal of a right triangle. If the speed of light is the same value in both reference frames, then the time interval between reflections (and clock ticks) will be longer in the lab frame now than for the clock at rest. Therefore, a moving clock ticks slower than an identical clock at rest. And this phenomenon is true for all clocks, no matter how they are made. A more complicated situation occurs when the light clock is accelerated parallel to the mirrors. We suggest that you think about this case when there is ample time in your schedule.
 الاكثر قراءة في طرائف الفيزياء
الاكثر قراءة في طرائف الفيزياء
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















