

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Phase transition
المؤلف:
Peter Atkins، Julio de Paula
المصدر:
ATKINS PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
الجزء والصفحة:
ص87-88
2025-11-05
410
Phase transition
The degree of dispersal of matter and energy changes when a substance freezes or boils as a result of changes in the order with which the molecules pack together and the extent to which the energy is localized or dispersed. Therefore, we should expect the transition to be accompanied by a change in entropy. For example, when a substance vaporizes, a compact condensed phase changes into a widely dispersed gas and we can expect the entropy of the substance to increase considerably. The entropy of a solid also increases when it melts to a liquid and when that liquid turns into a gas. Consider a system and its surroundings at the normal transition temperature, Ttrs , the temperature at which two phases are in equilibrium at 1 atm. This temper ature is 0°C (273 K) for ice in equilibrium with liquid water at 1 atm, and 100°C (373 K) for water in equilibrium with its vapour at 1 atm. At the transition temperature, any transfer of energy as heat between the system and its surroundings is reversible
because the two phases in the system are in equilibrium. Because at constant pressure q =∆trsH, the change in molar entropy of the system is4
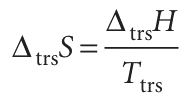
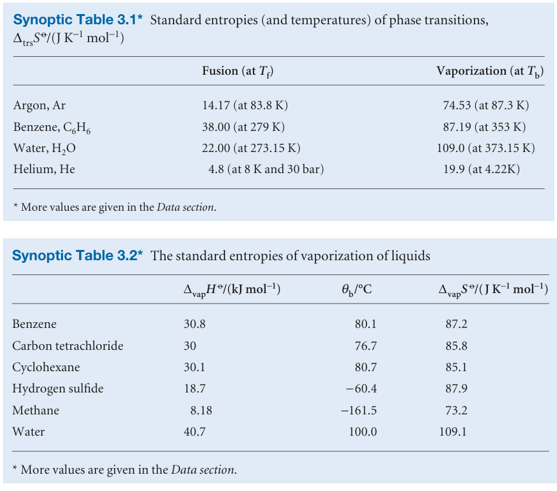
If the phase transition is exothermic (∆trsH < 0, as in freezing or condensing), then the entropy change is negative. This decrease in entropy is consistent with localization of matter and energy that accompanies the formation of a solid from a liquid or a liquid from a gas. If the transition is endothermic (∆trsH > 0, as in melting and vaporization), then the entropy change is positive, which is consistent with dispersal of energy and matter in the system. Table 3.1 lists some experimental entropies of transition. Table 3.2 lists in more detail the standard entropies of vaporization of several liquids at their boiling points. An interesting feature of the data is that a wide range of liquids give approximately the same standard entropy of vaporization (about 85 J K−1 mol−1): this empirical observation is called Trouton’s rule.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















