

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Solution methods
المؤلف:
Peter Atkins, Tina Overton, Jonathan Rourke, Mark Weller, and Fraser Armstrong
المصدر:
Shriver and Atkins Inorganic Chemistry ,5th E
الجزء والصفحة:
603-604
2025-10-08
148
Solution methods
Key point: Frameworks formed from polyhedral species can often be obtained by condensation reactions in solution. Many inorganic materials, especially framework structures, can be synthesized by crystallization from solution. Although the methods used are very diverse, the following are typical reactions that occur in water:
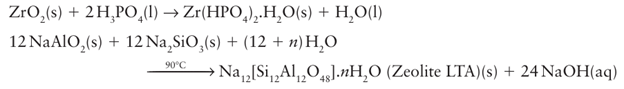
Solution methods are extended by using hydrothermal techniques, in which the reacting solution is heated above its normal boiling point in a sealed vessel. Such reactions are important for the synthesis of open-structure aluminosilicates (zeolites), analogous porous structures based on linked oxo-polyhedra (Section 24.13a), and related metal-organic frameworks (MOF) in which metal ions are linked by coordinating organic species, such as carboxylates (Section 24.13b). These porous structures are often thermodynamically metastable with respect as conversion to denser structure types so they cannot be made by direct high-temperature reactions. For example, the sodium aluminosilicate zeolite Na12 [Si12Al12 O48]. nH2O formed in solution converts on heating above 800°C to the dense aluminosilicate NaSiAlO4. More recently, other solvents such as liquid ammonia, super critical CO2, and organic amines have been used in so-called solvothermal reactions. A reaction in solution can also be used as an initial stage in the synthesis of many materials, particularly oxides, normally obtained through direct high-temperature reaction. The advantages of starting with solutions is that the reactants are mixed at the atomic level, so overcoming the problems associated with the direct reaction of two or more solid phases consisting of micrometre-sized particles. In the simplest reaction of this type, a solution of metal ions (for example, solutions of metal nitrates) is converted to a solid through a variety of methods such as evaporation of the solvent, precipitation as a simple mixed metal salt, or formation of a gel. This solid is then heated to produce the target material. Two examples are
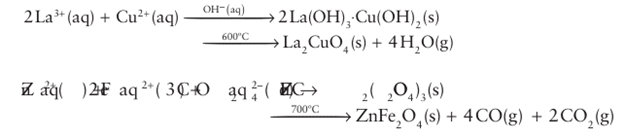
As well as the advantages of reduced reaction times, a result of the intimate mixing of the reactants, the final decomposition temperature is somewhat lower than that needed for the direct reaction of the oxides. The use of a lower temperature can also have the effect of reducing the size of the particles formed in the reaction. Further discussion of routes involving gel formation, or so-called ‘sol–gel processes’, are included in Sections 24.8 and 25.4. Although high-temperature direct-combination methods and solvothermal techniques are the most commonly used methods in materials chemistry, some reactions involving sol ids can occur at low temperatures if there is no major change in structure. These so-called ‘intercalation reactions’ are discussed in Section 24.10.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















