
Cytokines of Innate Immunity
 المؤلف:
Abbas, A. K., Lichtman, A. H., & Pillai, S
المؤلف:
Abbas, A. K., Lichtman, A. H., & Pillai, S
 المصدر:
Basic Immunology : Function and disorders of immune system
المصدر:
Basic Immunology : Function and disorders of immune system
 الجزء والصفحة:
6th ed , page 41-42
الجزء والصفحة:
6th ed , page 41-42
 2025-01-16
2025-01-16
 1113
1113
In response to microbes, dendritic cells, macrophages, mast cells and other cells secrete cytokines that mediate many of the cellular reactions of innate immunity (Fig. 1). As mentioned earlier, cytokines are soluble proteins that mediate immune and inflammatory reactions and are responsible for communications between leukocytes and between leukocytes and other cells. Most of the molecularly defined cytokines are called interleukins with a number, for example interleukin-1, but several have other names, for example tumor necrosis factor, for historical reasons related to how they were discovered. In innate immunity, the principal sources of cytokines are dendritic cells, macrophages, and mast cells that are activated by recognition of microbes, although epithelial cells and other cell types also secrete cytokines. Recognition of bacterial cell wall components such as LPS and peptidoglycan by TLRs and recognition of microbial nucleic acids by TLRs, RLRs, and CDSs are powerful stimuli for cytokine secretion by macrophages, dendritic cells, and many tissue cells. In adaptive immunity, helper T lymphocytes are a major source of cytokines.
Cytokines are secreted in small amounts in response to an external stimulus and bind to high-affinity receptors on target cells. Most cytokines act on nearby cells (paracrine actions), and some act on the cells that produce them (autocrine actions). In innate immune reactions against infections, enough dendritic cells and macrophages may be activated that large amounts of cytokines are produced, and they may be active distant from their site of secretion (endocrine actions). T he cytokines of innate immunity serve various functions in host defense. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF), interleukin-1 (IL-1), and chemokines (chemoattractant cytokines) are the principal cytokines involved in recruiting blood neutrophils and monocytes to sites of infection (described later). TNF and IL-1 also have systemic effects, including inducing fever by acting on the hypothalamus, and these cytokines as well as IL-6 stimulate liver cells to produce various proteins of the acute phase response, such as C-reactive protein and fibrinogen, which contribute to microbial killing and walling off infectious sites. At high concentrations, TNF promotes thrombus formation on the endothelium and reduces blood pressure by a combination of reduced myocardial contractility and vascular dilation and leakiness. Severe, disseminated bacterial infections sometimes lead to a potentially lethal clinical syndrome called septic shock, which is characterized by low blood pressure (the defining feature of shock), disseminated intravascular coagulation, and metabolic disturbances. The early clinical and pathologic manifestations of septic shock may be caused by high levels of TNF, which is produced in response to the bacteria. Dendritic cells and macrophages also produce IL-12 in response to LPS and other microbial molecules. The role of IL-12 in activating NK cells, ultimately leading to increased killing activity and macrophage activation, was mentioned previously. NK cells produce IFN-γ, whose function as a macrophage-activating cytokine was also described earlier. Because IFN-γ is produced by T cells as well, it is considered a cytokine of both innate immunity and adaptive immunity. In viral infections, a subset of dendritic cells, and to a lesser extent other infected cells, produce type I IFNs, which inhibit viral replication and prevent spread of the infection to uninfected cells.
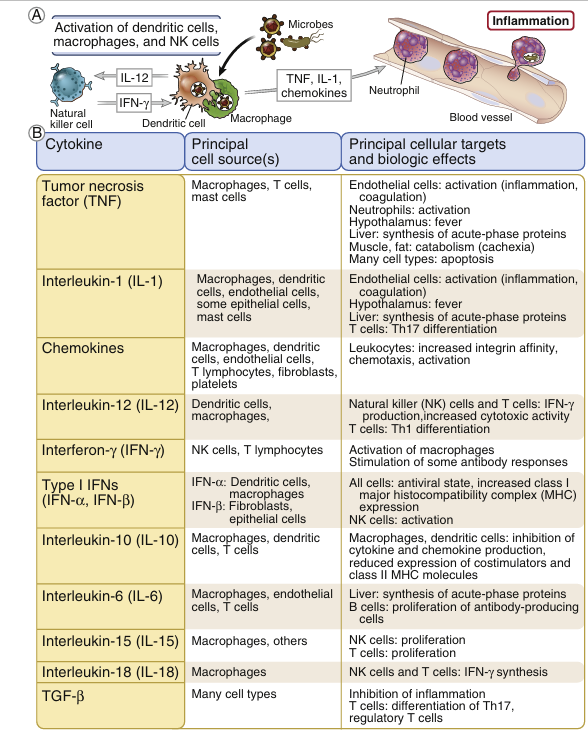
Fig. 1 Cytokines of innate immunity. A, Dendritic cells, macrophages, and other cells (such as mast cells and ILCs, not shown) respond to microbes by producing cytokines that stimulate inflammation (leukocyte recruitment) and activate natural killer (NK) cells to produce the macrophage-activating cytokine interferon-γ (IFN-γ). B, Some important characteristics of the major cytokines of innate immunity are listed. Note that IFN-γ and transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) are cytokines of both innate and adaptive immunity.
 الاكثر قراءة في المناعة
الاكثر قراءة في المناعة
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


