
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
Planetary motions
المؤلف:
Richard Feynman, Robert Leighton and Matthew Sands
المصدر:
The Feynman Lectures on Physics
الجزء والصفحة:
Volume I, Chapter 7
2024-01-31
1565
In this chapter we shall discuss one of the most far-reaching generalizations of the human mind. While we are admiring the human mind, we should take some time off to stand in awe of a nature that could follow with such completeness and generality such an elegantly simple principle as the law of gravitation. What is this law of gravitation? It is that every object in the universe attracts every other object with a force which for any two bodies is proportional to the mass of each and varies inversely as the square of the distance between them. This statement can be expressed mathematically by the equation
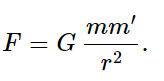
If to this we add the fact that an object responds to a force by accelerating in the direction of the force by an amount that is inversely proportional to the mass of the object, we shall have said everything required, for a sufficiently talented mathematician could then deduce all the consequences of these two principles. However, since you are not assumed to be sufficiently talented yet, we shall discuss the consequences in more detail, and not just leave you with only these two bare principles. We shall briefly relate the story of the discovery of the law of gravitation and discuss some of its consequences, its effects on history, the mysteries that such a law entails, and some refinements of the law made by Einstein; we shall also discuss the relationships of the law to the other laws of physics. All this cannot be done in one chapter, but these subjects will be treated in due time in subsequent chapters.
The story begins with the ancients observing the motions of planets among the stars, and finally deducing that they went around the sun, a fact that was rediscovered later by Copernicus. Exactly how the planets went around the sun, with exactly what motion, took a little more work to discover. Beginning in the sixteenth century there were great debates as to whether they really went around the sun or not. Tycho Brahe had an idea that was different from anything proposed by the ancients: his idea was that these debates about the nature of the motions of the planets would best be resolved if the actual positions of the planets in the sky were measured sufficiently accurately. If measurement showed exactly how the planets moved, then perhaps it would be possible to establish one or another viewpoint. This was a tremendous idea—that to find something out, it is better to perform some careful experiments than to carry on deep philosophical arguments. Pursuing this idea, Tycho Brahe studied the positions of the planets for many years in his observatory on the island of Hven, near Copenhagen. He made voluminous tables, which were then studied by the mathematician Kepler, after Tycho’s death. Kepler discovered from the data some very beautiful and remarkable, but simple, laws regarding planetary motion.
 الاكثر قراءة في الميكانيك
الاكثر قراءة في الميكانيك
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















