

Grammar


Tenses


Present

Present Simple

Present Continuous

Present Perfect

Present Perfect Continuous


Past

Past Continuous

Past Perfect

Past Perfect Continuous

Past Simple


Future

Future Simple

Future Continuous

Future Perfect

Future Perfect Continuous

Passive and Active


Parts Of Speech


Nouns

Countable and uncountable nouns

Verbal nouns

Singular and Plural nouns

Proper nouns

Nouns gender

Nouns definition

Concrete nouns

Abstract nouns

Common nouns

Collective nouns

Definition Of Nouns


Verbs

Stative and dynamic verbs

Finite and nonfinite verbs

To be verbs

Transitive and intransitive verbs

Auxiliary verbs

Modal verbs

Regular and irregular verbs

Action verbs


Adverbs

Relative adverbs

Interrogative adverbs

Adverbs of time

Adverbs of place

Adverbs of reason

Adverbs of quantity

Adverbs of manner

Adverbs of frequency

Adverbs of affirmation


Adjectives

Quantitative adjective

Proper adjective

Possessive adjective

Numeral adjective

Interrogative adjective

Distributive adjective

Descriptive adjective

Demonstrative adjective


Pronouns

Subject pronoun

Relative pronoun

Reflexive pronoun

Reciprocal pronoun

Possessive pronoun

Personal pronoun

Interrogative pronoun

Indefinite pronoun

Emphatic pronoun

Distributive pronoun

Demonstrative pronoun


Pre Position


Preposition by function

Time preposition

Reason preposition

Possession preposition

Place preposition

Phrases preposition

Origin preposition

Measure preposition

Direction preposition

Contrast preposition

Agent preposition


Preposition by construction

Simple preposition

Phrase preposition

Double preposition

Compound preposition


Conjunctions

Subordinating conjunction

Correlative conjunction

Coordinating conjunction

Conjunctive adverbs


Interjections

Express calling interjection


Grammar Rules

Preference

Requests and offers

wishes

Be used to

Some and any

Could have done

Describing people

Giving advices

Possession

Comparative and superlative

Giving Reason

Making Suggestions

Apologizing

Forming questions

Since and for

Directions

Obligation

Adverbials

invitation

Articles

Imaginary condition

Zero conditional

First conditional

Second conditional

Third conditional

Reported speech


Linguistics

Phonetics

Phonology


Semantics


Pragmatics

Linguistics fields

Syntax

Morphology

Semantics

pragmatics

History

Writing

Grammar

Phonetics and Phonology


Reading Comprehension

Elementary

Intermediate

Advanced
NUMBER
المؤلف:
David Hornsby
المصدر:
Linguistics A complete introduction
الجزء والصفحة:
124-6
2023-12-19
954
NUMBER
The category of number in English primarily affects nouns, and only minimally verbs (for example, in the was/were singular/ plural opposition for the verb to be), and has the values singular and plural, the latter as we have seen being generally marked by a suffix to a nominal stem. From an anglophone perspective, it is easy to assume that these are the only two relevant values, but number systems like that of English do not in fact represent the norm cross-linguistically.
A few languages, for example Pirahã (spoken by around 250 people in Amazonas, Brazil), are believed to have no category of number, while others have systems which mark not just singular and plural but singular, dual (inflection for two items), trial (for three) or paucal (a small number of items). The pronoun system of Sursurunga, a language spoken in New Ireland, Papua New Guinea, has a five-value system that distinguishes singular, dual, trial, quadral (for four items) and plural in its pronoun system:
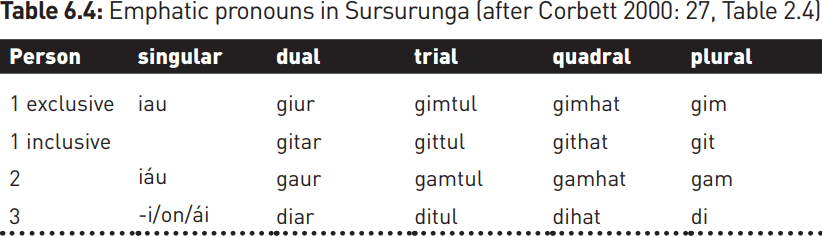
The number category differs not only in the number of values expressed in different languages, but also in the way these values are expressed. In English, for example, nouns must generally be marked singular or plural, but in some languages there is an unspecified or general form which commits the speaker to no number value. In the Bayso language of Southern Ethiopia, for example, the base form of the noun is unmarked for number, and there are separate suffixes for singular, paucal and plural (2000: 11):
