

النبات

مواضيع عامة في علم النبات

الجذور - السيقان - الأوراق

النباتات الوعائية واللاوعائية

البذور (مغطاة البذور - عاريات البذور)

الطحالب

النباتات الطبية


الحيوان

مواضيع عامة في علم الحيوان

علم التشريح

التنوع الإحيائي

البايلوجيا الخلوية


الأحياء المجهرية

البكتيريا

الفطريات

الطفيليات

الفايروسات


علم الأمراض

الاورام

الامراض الوراثية

الامراض المناعية

الامراض المدارية

اضطرابات الدورة الدموية

مواضيع عامة في علم الامراض

الحشرات


التقانة الإحيائية

مواضيع عامة في التقانة الإحيائية


التقنية الحيوية المكروبية

التقنية الحيوية والميكروبات

الفعاليات الحيوية

وراثة الاحياء المجهرية

تصنيف الاحياء المجهرية

الاحياء المجهرية في الطبيعة

أيض الاجهاد

التقنية الحيوية والبيئة

التقنية الحيوية والطب

التقنية الحيوية والزراعة

التقنية الحيوية والصناعة

التقنية الحيوية والطاقة

البحار والطحالب الصغيرة

عزل البروتين

هندسة الجينات


التقنية الحياتية النانوية

مفاهيم التقنية الحيوية النانوية

التراكيب النانوية والمجاهر المستخدمة في رؤيتها

تصنيع وتخليق المواد النانوية

تطبيقات التقنية النانوية والحيوية النانوية

الرقائق والمتحسسات الحيوية

المصفوفات المجهرية وحاسوب الدنا

اللقاحات

البيئة والتلوث


علم الأجنة

اعضاء التكاثر وتشكل الاعراس

الاخصاب

التشطر

العصيبة وتشكل الجسيدات

تشكل اللواحق الجنينية

تكون المعيدة وظهور الطبقات الجنينية

مقدمة لعلم الاجنة


الأحياء الجزيئي

مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي


علم وظائف الأعضاء


الغدد

مواضيع عامة في الغدد

الغدد الصم و هرموناتها

الجسم تحت السريري

الغدة النخامية

الغدة الكظرية

الغدة التناسلية

الغدة الدرقية والجار الدرقية

الغدة البنكرياسية

الغدة الصنوبرية

مواضيع عامة في علم وظائف الاعضاء

الخلية الحيوانية

الجهاز العصبي

أعضاء الحس

الجهاز العضلي

السوائل الجسمية

الجهاز الدوري والليمف

الجهاز التنفسي

الجهاز الهضمي

الجهاز البولي


المضادات الميكروبية

مواضيع عامة في المضادات الميكروبية

مضادات البكتيريا

مضادات الفطريات

مضادات الطفيليات

مضادات الفايروسات

علم الخلية

الوراثة

الأحياء العامة

المناعة

التحليلات المرضية

الكيمياء الحيوية

مواضيع متنوعة أخرى

الانزيمات
Prostaglandin and Thromboxane Synthesis
المؤلف:
Denise R. Ferrier
المصدر:
Lippincott Illustrated Reviews: Biochemistry
الجزء والصفحة:
16-10-2021
2417
Prostaglandin and Thromboxane Synthesis
Arachidonic acid, an ω-6 FA containing 20 carbons and four double bonds (an eicosatetraenoic FA), is the immediate precursor of the predominant type of human PG (series 2 or those with two double bonds, as shown in Fig. 1). It is derived by the elongation and desaturation of the essential FA linoleic acid, also an ω-6 FA. Arachidonic acid is incorporated into membrane phospholipids (typically PI) at carbon 2, from which it is released by phospholipase A2 (Fig. 2) in response to a variety of signals, such as a rise in calcium. [Note: Series 1 PG contain one double bond and are derived from an ω-6 eicosatrienoic FA, dihomo-γ-linolenic acid, whereas series 3 PG contain three double bonds and are derived from eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), an ω-3 FA.]

Figure 1: Oxidation and cyclization of arachidonic acid by the two catalytic activities (cyclooxygenase and peroxidase) of PGH2 synthase (prostaglandin endoperoxide synthase). G-SH = reduced glutathione; G-S-S-G = oxidized glutathione; PG = prostaglandin.
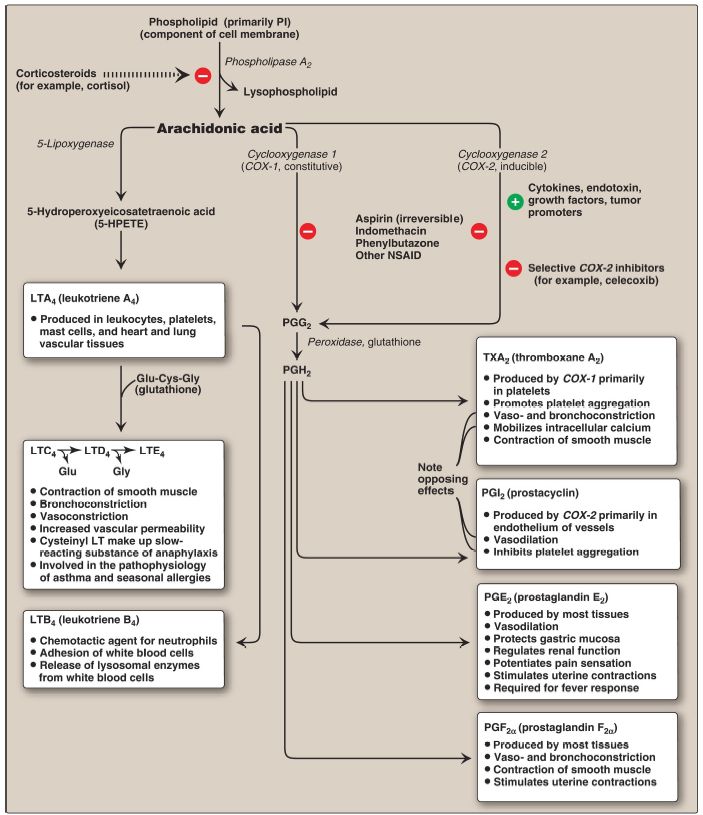
Figure 2: Overview of the biosynthesis and function of some important prostaglandins (PG), leukotrienes (LT), and a thromboxane (TX) from arachidonic acid. [Note: The arachidonic acid in the membrane phospholipid was derived from the ω-6 essential fatty acid (FA), linoleic, also an ω-6 FA.] PI = phosphatidylinositol; NSAID = nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs; Glu = glutamate; Cys = cysteine; Gly = glycine.
1. Prostaglandin H2 synthase: The first step in PG and TX synthesis is the oxidative cyclization of free arachidonic acid to yield PGH2 by PGH2 synthase (or, prostaglandin endoperoxide synthase). This enzyme is an ER membrane-bound protein that has two catalytic activities: fatty acid cyclooxygenase (COX), which requires two molecules of O2, and peroxidase, which requires reduced glutathione . PGH2 is converted to a variety of PG and TX, as shown in Figure 2, by cellspecific synthases. [Note: PG contain a five-carbon ring, whereas TX contain a heterocyclic six-membered oxane ring .] Two isozymes of PGH2 synthase, usually denoted as COX-1 and COX-2, are known. COX-1 is made constitutively in most tissues and is required for maintenance of healthy gastric tissue, renal homeostasis, and platelet aggregation. COX-2 is inducible in a limited number of tissues in response to products of activated immune and inflammatory cells. [Note: The increase in PG synthesis subsequent to the induction of COX-2 mediates the pain, heat, redness, and swelling of inflammation and the fever of infection.]
2. Synthesis inhibition: The synthesis of PG and TX can be inhibited by unrelated compounds. For example, cortisol (a steroidal antiinflammatory agent) inhibits phospholipase A2 activity (see Fig. 2) and, therefore, arachidonic acid, the substrate for PG and TX synthesis, is not released from membrane phospholipids. Aspirin, indomethacin, and phenylbutazone (all nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs [NSAID]) inhibit both COX-1 and COX-2 and, thus, prevent the synthesis of the parent molecule, PGH2. [Note: Systemic inhibition of COX-1, with subsequent damage to the stomach and the kidneys and impaired clotting of blood, is the basis of aspirin’s toxicity.] Aspirin (but not other NSAID) also induces synthesis of lipoxins (anti-inflammatory mediators made from arachidonic acid) and resolvins and protectins (inflammationresolving mediators made from EPA). Inhibitors specific for COX-2 (the coxibs, for example, celecoxib) were designed to reduce pathologic inflammatory processes mediated by COX-2 while maintaining the physiologic functions of COX-1. However, their use has been associated with increased risk of heart attacks, likely as a result of decreased PGI2 synthesis (see B. below), and some have been withdrawn from the market.
 الاكثر قراءة في الكيمياء الحيوية
الاكثر قراءة في الكيمياء الحيوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















