
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
Picosecond Lasers
المؤلف:
Walter Koechner Michael Bass
المصدر:
Solid-state Lasers
الجزء والصفحة:
326
22-1-2021
1801
Picosecond Lasers
Today, diode-pumped cw Nd :YAG or Nd : YLF lasers, mode-locked with an acousto-optic modulator, are the standard sources for the production of picosecond pulses. A typically end-pumped and actively mode-locked neodymium laser is shown in Fig. 1. The output from a GaAlAs diode array is focused onto the end of the laser crystal. Spot sizes of the pump beam range from 50μm to a few hundred micrometers. A common resonator configuration for diode-pumped actively mode-locked lasers is a three-mirror arrangement. A folded cavity geometry provides a beam waist at both the laser crystal and the modulator, as well as astigmatic compensation. In commercial mode-locked lasers, the resonator is usually folded a few times to decrease the overall length of the system. The length of the cavity is usually a compromise between the need for short pulses, which requires a short resonator and a high-modulation frequency, and the ability to slice out a single pulse with a Pockels cell.
Typical of end-pumped lasers is the highly reflective coating applied to the back face of the crystal (Fig. 1) to form one of the resonator mirrors. Small thermal or vibrational changes in the pump radiation readily induce relaxation
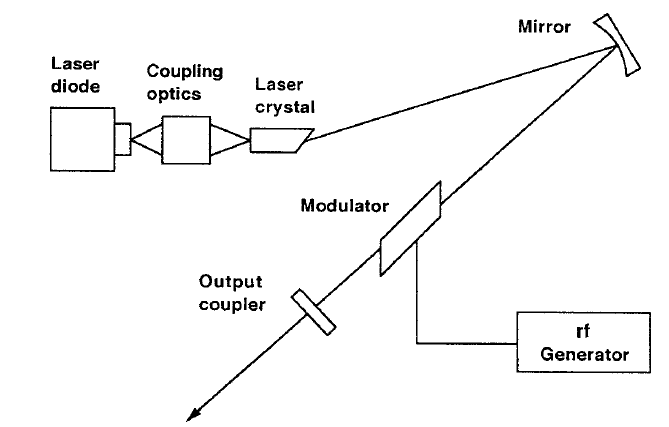
FIGURE 1. Typical end-pumped and actively mode-locked neodymium laser.
oscillations in mode-locked systems. These relaxation oscillations cause fluctuations in amplitude, accompanied by damped oscillations at frequencies in the 30 to 150 kHz range. Therefore, careful alignment and isolation is required for clean mode-locking. The modulator is usually placed close to the front mirror at the beam waist created by the folding mirror. The resonator length is typically on the order of 1m or longer to provide a sufficiently large separation between pulses for pulse selection by an external switching device. Actively mode-locked lasers are very sensitive to cavity length detuning. In practice, cavity length changes on the order of 1μm can cause serious degradation in pulse quality. Therefore, active length stabilization of the resonator by a feedback loop is needed to maintain long-term stability of mode-locking.
Active mode-locking of a laser can be achieved by using a tunable rf oscillator and adjusting the modulator frequency to agree with the cavity length; or, alternatively, selecting a fixed frequency and adjusting the mirror spacing.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الليزر
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الليزر
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















