
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء والفلسفة

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
Diffraction Losses
المؤلف:
Walter Koechner, Michael Bass
المصدر:
Solid-State Lasers
الجزء والصفحة:
163
20-1-2021
2251
Diffraction Losses
In any real laser resonator some part of the laser beam will be lost either by spillover at the mirrors or by limiting apertures, such as the lateral boundaries of the active material. These losses will depend on the diameter of the laser beam in the plane of the aperture and the aperture radius. If we take a finite aperture of radius a within the resonator into account, the diffraction losses depend on four parameters, R1, R2, L, and a, which describe the resonator; and on three parameters λ, m, and n, characterizing the particular mode present in the resonator. Fortunately, the losses depend only on certain combinations of these parameters. These combinations are the so-called Fresnel number, rameters λ, m, and n, characterizing the particular mode present in the resonator.
Fortunately, the losses depend only on certain combinations of these parameters.
These combinations are the so-called Fresnel number,
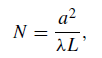 ........(1)
........(1)
and the quantities g1 and g2. The parameter N can be thought of as the ratio of the acceptance angle (a/L) of one mirror as viewed from the center of the opposing mirror to the diffraction angle (λ/a) of the beam. Therefore, when N is small, especially if N < 1, the loss factor will be high because only a portion of the beam will be intercepted by the mirrors.
Conversely when N is large, diffraction losses will be low. The fractional energy loss per transit because of diffraction effects for the lowest-order mode (TEM00) is shown in Fig. 1 for resonators with equally curved mirrors and apertures located in front of the mirrors (g1 = g2 = g, a1 = a2 = a). The plane-parallel and concentric resonator (|g| = 1) have the highest losses for a
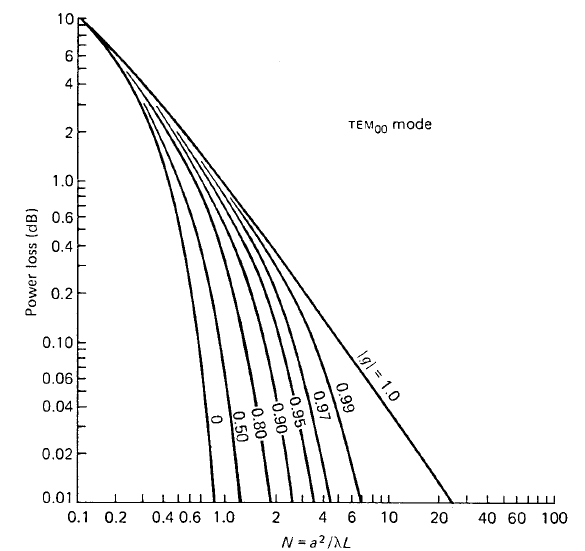
FIGURE 1. Diffraction losses per transit for the TEM00 mode of various symmetrical
resonators.
given aperture according to Fig. 1. This is not surprising because both resonator configurations have mode sizes which approach infinity at the limit. On the other hand, the confocal resonator (g = 0) has the smallest mode dimension for a given resonator length as discussed before. Therefore a given aperture will also cause the lowest diffraction losses. It can also be seen from Fig. 1 that the diffraction losses are very sensitive to changes in mirror curvature, and losses decrease very rapidly for all resonator configurations as N increases.
Mode selection or discrimination of higher order modes, by choosing the appropriate Fresnel number, that is, intracavity aperture. In this figure, the diffraction losses in a confocal resonator for a number of low-order modes are plotted versus the Fresnel number. For N = 1, only the TEM00 and the TEM01 modes have a power loss per transit of less than 1% per pass. All other modes have losses above 10%. A laser with this resonator would emit on only these two modes if the gain per pass were less than 10%. Single-mode emission would require a slightly smaller aperture to reduce the value of N just under 1. Going in the other direction, if the aperture is increased by about a factor of 1.4 in diameter to yield F = 2, then 10 modes from TEM00 to TEM05 have less than 1% loss per transit. This resonator would clearly have a multimode output.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الليزر
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الليزر
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















