


 النبات
النبات
 الحيوان
الحيوان
 الأحياء المجهرية
الأحياء المجهرية
 علم الأمراض
علم الأمراض
 التقانة الإحيائية
التقانة الإحيائية
 التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
 التقنية الحياتية النانوية
التقنية الحياتية النانوية
 علم الأجنة
علم الأجنة
 الأحياء الجزيئي
الأحياء الجزيئي
 علم وظائف الأعضاء
علم وظائف الأعضاء
 الغدد
الغدد
 المضادات الحيوية
المضادات الحيوية|
Read More
Date: 25-4-2016
Date: 24-12-2015
Date: 9-5-2016
|
Radiation Hybrid Mapping
Radiation hybrid mapping is a genetic technique that was originally developed for constructing long-range maps of mammalian chromosomes. It is based on a statistical method to determine not only the distances between deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) markers but also their order on the chromosomes. DNA markers are short, repetitive DNA sequences, most often located in noncoding regions of the genome, that have proven extremely valuable for localizing human disease genes in the genome.
Theory and Application
In radiation hybrid mapping, human chromosomes are separated from one another and broken into several fragments using high doses of X rays. Similar to the underlying principle of mapping genes by linkage analysis based on recombination events, the farther apart two DNA markers are on a chromosome, the more likely a given dose of X rays will break the chromosome between them and thus place the two markers on two different chromosomal fragments. The order of markers on a chromosome can be determined by estimating the frequency of breakage that, in turn, depends on the distance between the markers. This technique has been used to construct whole-genome radiation hybrid maps.
Technique
A rodent-human somatic cell hybrid (“artificial” cells with both rodent and human genetic material), which contains a single copy of the human chromosome of interest, is X-irradiated. This breaks the chromosome into several pieces, which are subsequently integrated into the rodent chromosomes. In addition, the dosage of radiation is sufficient to kill the somatic cell hybrid or donor cells, which are then rescued by fusing them with nonirradiated rodent recipient cells. The latter, however, lack an important enzyme and are also killed when grown in a specific medium. Therefore, the only cells that can survive the procedure are donor-recipient hybrids that have acquired a rodent gene for the essential enzyme from the irradiated rodent- human cell line
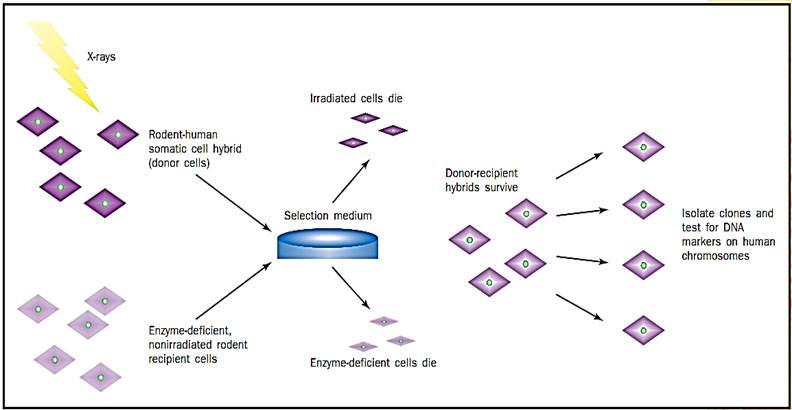
Radiation hybrid mapping process.
From these donor-recipient hybrids, clones can be isolated and tested for the presence or absence of DNA markers on the human chromosome of interest, and the frequencies with which markers were retained in each clone can be calculated. This process is complicated by the fact that hybrids may contain more than one DNA fragment. For example, two markers retained in one hybrid may result from retention of the two markers on separate fragments or from no break between the markers. However, the frequency of breakage, theta, can be estimated using statistical methods, and a lod score (logarithm of the likelihood ratio for linkage) can be calculated to identify significantly linked marker pairs.
References
Cox, David R., Margit Burmeister, Price E. Roydon, Suwon Kim, and Richard M. Myers. “Radiation Hybrid Mapping: A Somatic Cell Genetic Method for Constructing High-Resolution Maps of Mammalian Chromosomes.” Science 250 (1990): 245-250.
Goss S. J., and H. Harris. “New Method for Mapping Genes in Human Chromosomes.” Nature 255 (1975): 680-684.
Rutgers University. http://compgen.rutgers.edu/rhmap/.
Watson, James D., Michael Gilman, Jan Witkowski, and M. Zoller. Recombinant DNA, 2nd ed. New York: W. H. Freeman and Company, 1993.



|
|
|
|
للعاملين في الليل.. حيلة صحية تجنبكم خطر هذا النوع من العمل
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
"ناسا" تحتفي برائد الفضاء السوفياتي يوري غاغارين
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
بمناسبة مرور 40 يومًا على رحيله الهيأة العليا لإحياء التراث تعقد ندوة ثقافية لاستذكار العلامة المحقق السيد محمد رضا الجلالي
|
|
|