


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 22-8-2019
Date: 28-7-2018
Date: 5-8-2018
|
The resonance effect described here is undoubtedly the major contributor to the exceptional acidity of carboxylic acids. However, inductive effects also play a role. For example, alcohols have pKa's of 16 or greater but their acidity is increased by electron withdrawing substituents on the alkyl group. The following diagram illustrates this factor for several simple inorganic and organic compounds (row #1), and shows how inductive electron withdrawal may also increase the acidity of carboxylic acids (rows #2 & 3). The acidic hydrogen is colored red in all examples.
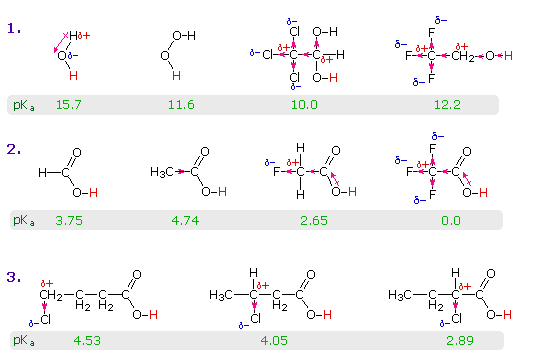
Water is less acidic than hydrogen peroxide because hydrogen is less electronegative than oxygen, and the covalent bond joining these atoms is polarized in the manner shown. Alcohols are slightly less acidic than water, due to the poor electronegativity of carbon, but chloral hydrate, Cl3CCH(OH)2, and 2,2,2,-trifluoroethanol are significantly more acidic than water, due to inductive electron withdrawal by the electronegative halogens (and the second oxygen in chloral hydrate). In the case of carboxylic acids, if the electrophilic character of the carbonyl carbon is decreased the acidity of the carboxylic acid will also decrease. Similarly, an increase in its electrophilicity will increase the acidity of the acid. Acetic acid is ten times weaker an acid than formic acid (first two entries in the second row), confirming the electron donating character of an alkyl group relative to hydrogen, as noted earlier in a discussion of carbocation stability. Electronegative substituents increase acidity by inductive electron withdrawal. As expected, the higher the electronegativity of the substituent the greater the increase in acidity (F > Cl > Br > I), and the closer the substituent is to the carboxyl group the greater is its effect (isomers in the 3rd row). Substituents also influence the acidity of benzoic acid derivatives, but resonance effects compete with inductive effects. The methoxy group is electron donating and the nitro group is electron withdrawing (last three entries in the table of pKa values).



|
|
|
|
لخفض ضغط الدم.. دراسة تحدد "تمارين مهمة"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
طال انتظارها.. ميزة جديدة من "واتساب" تعزز الخصوصية
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
مشاتل الكفيل تزيّن مجمّع أبي الفضل العبّاس (عليه السلام) بالورد استعدادًا لحفل التخرج المركزي
|
|
|