x

هدف البحث
بحث في العناوين
بحث في المحتوى
بحث في اسماء الكتب
بحث في اسماء المؤلفين

اختر القسم
موافق


النبات

مواضيع عامة في علم النبات

الجذور - السيقان - الأوراق

النباتات الوعائية واللاوعائية

البذور (مغطاة البذور - عاريات البذور)

الطحالب

النباتات الطبية


الحيوان

مواضيع عامة في علم الحيوان

علم التشريح

التنوع الإحيائي

البايلوجيا الخلوية


الأحياء المجهرية

البكتيريا

الفطريات

الطفيليات

الفايروسات


علم الأمراض

الاورام

الامراض الوراثية

الامراض المناعية

الامراض المدارية

اضطرابات الدورة الدموية

مواضيع عامة في علم الامراض

الحشرات


التقانة الإحيائية

مواضيع عامة في التقانة الإحيائية


التقنية الحيوية المكروبية

التقنية الحيوية والميكروبات

الفعاليات الحيوية

وراثة الاحياء المجهرية

تصنيف الاحياء المجهرية

الاحياء المجهرية في الطبيعة

أيض الاجهاد

التقنية الحيوية والبيئة

التقنية الحيوية والطب

التقنية الحيوية والزراعة

التقنية الحيوية والصناعة

التقنية الحيوية والطاقة

البحار والطحالب الصغيرة

عزل البروتين

هندسة الجينات


التقنية الحياتية النانوية

مفاهيم التقنية الحيوية النانوية

التراكيب النانوية والمجاهر المستخدمة في رؤيتها

تصنيع وتخليق المواد النانوية

تطبيقات التقنية النانوية والحيوية النانوية

الرقائق والمتحسسات الحيوية

المصفوفات المجهرية وحاسوب الدنا

اللقاحات

البيئة والتلوث


علم الأجنة

اعضاء التكاثر وتشكل الاعراس

الاخصاب

التشطر

العصيبة وتشكل الجسيدات

تشكل اللواحق الجنينية

تكون المعيدة وظهور الطبقات الجنينية

مقدمة لعلم الاجنة


الأحياء الجزيئي

مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي


علم وظائف الأعضاء


الغدد

مواضيع عامة في الغدد

الغدد الصم و هرموناتها

الجسم تحت السريري

الغدة النخامية

الغدة الكظرية

الغدة التناسلية

الغدة الدرقية والجار الدرقية

الغدة البنكرياسية

الغدة الصنوبرية

مواضيع عامة في علم وظائف الاعضاء

الخلية الحيوانية

الجهاز العصبي

أعضاء الحس

الجهاز العضلي

السوائل الجسمية

الجهاز الدوري والليمف

الجهاز التنفسي

الجهاز الهضمي

الجهاز البولي


المضادات الحيوية

مواضيع عامة في المضادات الحيوية

مضادات البكتيريا

مضادات الفطريات

مضادات الطفيليات

مضادات الفايروسات

علم الخلية

الوراثة

الأحياء العامة

المناعة

التحليلات المرضية

الكيمياء الحيوية

مواضيع متنوعة أخرى

الانزيمات
Phospholipid
المؤلف:
Denise R. Ferrier
المصدر:
Lippincott Illustrated Reviews: Biochemistry
الجزء والصفحة:
18-10-2021
1526
Phospholipid
Phospholipids are polar, ionic compounds composed of an alcohol (for example, choline or ethanolamine) attached by a phosphodiester bond either to diacylglycerol (DAG), producing phosphatidylcholine or phosphatidylethanolamine, or to the amino alcohol sphingosine (Fig. 1). Addition of a long-chain fatty acid to sphingosine produces a ceramide. Addition of phosphorylcholine produces the phospholipid sphingomyelin.
Phospholipids are the predominant lipids of cell membranes. Nonmembrane phospholipids serve as components of lung surfactant and bile. Dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine, also called dipalmitoyl lecithin, is the major lipid component of lung surfactant.
Insufficient surfactant production causes respiratory distress syndrome. Phosphatidylinositol (PI) serves as a reservoir for arachidonic acid in membranes. The phosphorylation of membrane-bound PI produces phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2). This compound is degraded by phospholipase C in response to the binding of various neurotransmitters, hormones, and growth factors to membrane G protein–coupled receptors. The products of this degradation, inositol 1,4,5- trisphosphate (IP3) and DAG, mediate the mobilization of intracellular calcium and the activation of protein kinase C, which act synergistically to evoke cellular responses. Specific proteins can be covalently attached via a carbohydrate bridge to membrane-bound PI, forming a glycosyl phosphatidylinositol (GPI) anchor. A deficiency in GPI synthesis in hematopoietic cells results in the hemolytic disease paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. The degradation of phosphoglycerides is performed by phospholipases found in all tissues and pancreatic juice. Sphingomyelin is degraded to a ceramide plus phosphorylcholine by the lysosomal enzyme sphingomyelinase, a deficiency of which causes Niemann-Pick (A and B) disease. Glycosphingolipids are derivatives of ceramides to which carbohydrates have been attached. Adding one sugar molecule to the ceramide produces a cerebroside, adding an oligosaccharide produces a globoside, and adding an acidic N-acetylneuraminic acid molecule produces a ganglioside. Glycosphingolipids are found predominantly in cell membranes of the brain and peripheral nervous tissue, with high concentrations in the myelin sheath. They are antigenic. Glycolipids are degraded in the lysosomes by acid hydrolases. A deficiency of any one of these enzymes causes a sphingolipidosis, in which a characteristic sphingolipid accumulates. Prostaglandins (PG), thromboxanes (TX), and leukotrienes (LT), the eicosanoids, are produced in very small amounts in almost all tissues, act locally, and have an extremely short half-life. They serve as mediators of the inflammatory response. Arachidonic acid is the immediate precursor of the predominant class of human PG (those with two double bonds). It is derived by the elongation and desaturation of the essential fatty acid linoleic acid and is stored in the membrane as a component of a phospholipid, generally PI. Arachidonic acid is released from the phospholipid by phospholipase A2 (inhibited by cortisol).
Synthesis of the PG and TX begins with the oxidative cyclization of free arachidonic acid to yield PGH2 by PGH2 synthase (or, prostaglandin endoperoxide synthase), an endoplasmic reticular membrane protein that has two catalytic activities: fatty acid cyclooxygenase (COX) and peroxidase. There are two isozymes of PGH2 synthase: COX-1 (constitutive) and COX-2 (inducible). Aspirin irreversibly inhibits both. Opposing effects of PGI2 and TXA2 limit clot formation. LT are linear molecules produced from arachidonic acid by the 5-lipoxygenase (5-LOX) pathway. They mediate allergic response. Their synthesis is inhibited by cortisol and not by aspirin.
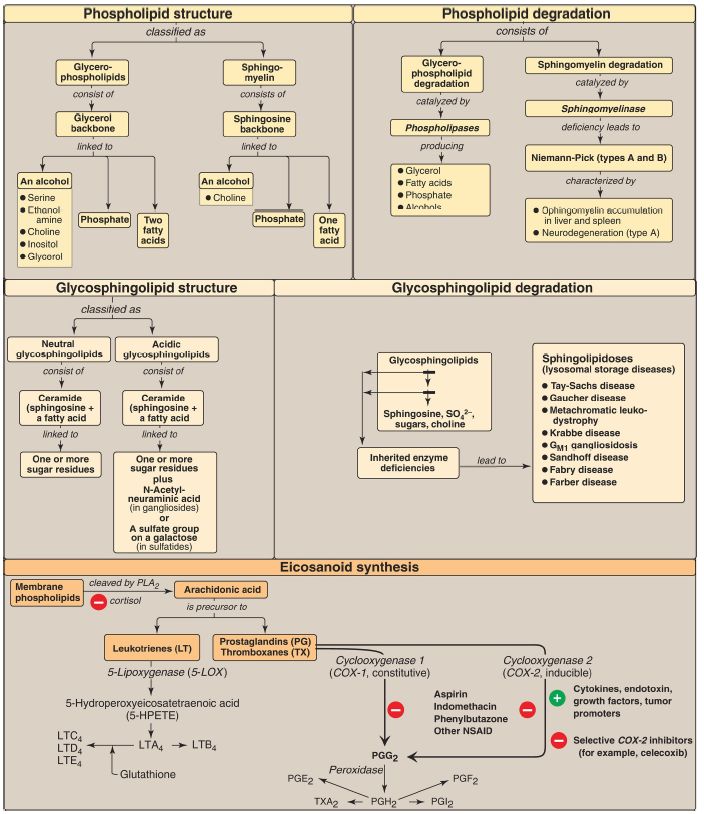
Figure 1: Key concept map for phospholipids, glycosphingolipids, and eicosanoids. PLA2 = phospholipase A2; SO4-2= sulfate ion; NSAID = nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.